假设我们给锁设置的过期时间太短,业务还没执行完成,锁就过期了,这块应该如何处理呢?是否可以给分布式锁续期?
解决方案:先设置一个过期时间,然后我们开启一个守护线程,定时去检测这个锁的失效时间,如果锁快要过期了,操作共享资源还未完成,那么就自动对锁进行续期,重新设置过期时间。
幸运的是有一个库把这些工作都帮我们封装好了,那就是 Redisson,Redisson 是 java 语言实现的 Redis SDK 客户端,它能给 Redis 分布式锁实现过期时间自动续期。
当然,Redisson 不只是会做这个,除此之外,还封装了很多易用的功能:
这里我们只讲怎么实现续期,有需要的小伙伴可以自己去了解其他的功能哦。
在使用分布式锁时,Redisson 采用了自动续期的方案来避免锁过期,这个守护线程我们一般也把它叫做 “看门狗(watch dog)” 线程。
watch dog自动延期机制
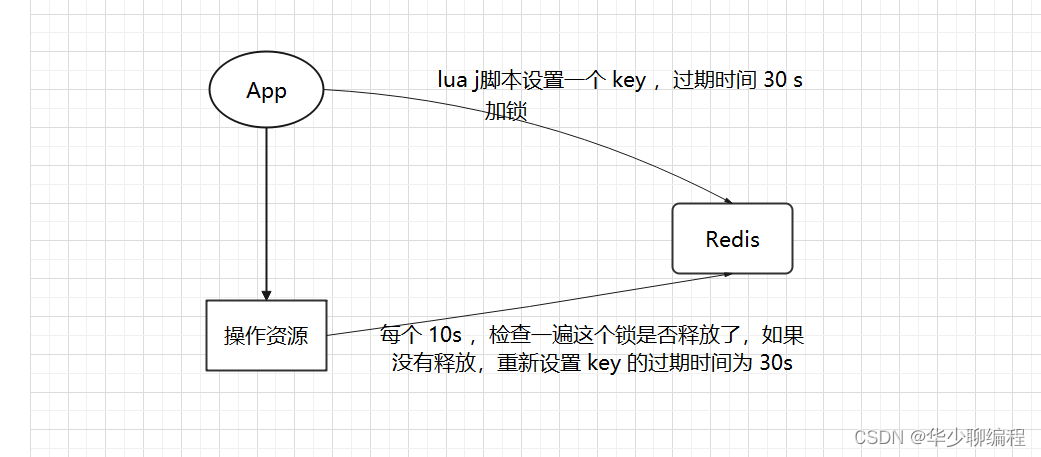
只要客户端一旦加锁成功,就会启动一个 watch dog 看门狗。watch dog 是一个后台线程,会每隔 10 秒检查一下,如果客户端还持有锁 key,那么就会不断的延长锁 key 的生存时间。
如果负责存储这个分布式锁的 Redission 节点宕机后,而且这个锁正好处于锁住的状态时,这个锁会出现锁死的状态,为了避免这种情况的发生,Redisson 提供了一个监控锁的看门狗,它的作用是在 Redisson 实例被关闭前,不断的延长锁的有效期。默认情况下,看门狗的续期时间是 30 秒,也可以通过修改 Config.lockWatchdogTimeout 来指定。
另外 Redisson 还提供了可以指定 leaseTime 参数的加锁方法来指定加锁的时间。超过这个时间后锁便自动解开了,不会延长锁的有效期。
接下来我们从源码看一下是怎么实现的。
源码分析
首先我们先写一个 dome 一步步点击进去看。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("MyLock");
lock.lock();
|
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(“MyLock”); 这句代码就是为了获取锁的实例,然后我们可以看到它返回的是一个 RedissonLock 对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
//name:锁的名称
public RLock getLock(String name) {
//默认创建的同步执行器, (存在异步执行器, 因为锁的获取和释放是有强一致性要求, 默认同步)
return new RedissonLock(this.connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
}
|
点击 RedissonLock 进去,发现这是一个 RedissonLock 构造方法,主要初始化一些属性。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
//唯一ID
this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
//等待获取锁时间
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
//ID + 锁名称
this.entryName = this.id + ":" + name;
//发布订阅
this.pubSub = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getSubscribeService().getLockPubSub();
}
|
我们点击 getLockWatchdogTimeout() 进去看一下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Config {
private long lockWatchdogTimeout = 30 * 1000;
public long getLockWatchdogTimeout() {
return lockWatchdogTimeout;
}
//省略
}
|
从 internalLockLeaseTime 这个单词也可以看出,这个加的分布式锁的超时时间默认是 30 秒,现在我们知道默认是 30 秒,那么这个看门狗多久时间来延长一次有效期呢?我们接着往下看。
这里我们选择 lock.lock(); 点击进去看:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public void lock() {
try {
this.lock(-1L, (TimeUnit)null, false);
} catch (InterruptedException var2) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl != null) {
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = this.subscribe(threadId);
if (interruptibly) {
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future);
} else {
this.commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
}
|
上面参数的含义:
leaseTime: 加锁到期时间, -1 使用默认值 30 秒
unit: 时间单位, 毫秒、秒、分钟、小时…
interruptibly: 是否可被中断标示
而 this.tryAcquire()这个方法中是用来执行加锁, 继续跳进去看:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
//执行 tryLock(...) 才会进入
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
//进行异步获取锁
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
//尝试异步获取锁, 获取锁成功返回空, 否则返回锁剩余过期时间
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
//ttlRemainingFuture 执行完成后触发此操作
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
//ttlRemaining == null 代表获取了锁
//获取到锁后执行续时操作
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}
|
我们继续选择 scheduleExpirationRenewal() 跳进去看:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry();
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
this.renewExpiration();
}
}
|
接着进去 renewExpiration() 方法看:
该方法就是开启定时任务,也就是 watch dog 去进行锁续期。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
private void renewExpiration() {
//从容器中去获取要被续期的锁
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());
//容器中没有要续期的锁,直接返回null
if (ee != null) {
//创建定时任务
//并且执行的时间为 30000/3 毫秒,也就是 10 秒后
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
//从容器中取出线程
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());
if (ent != null) {
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId != null) {
//Redis进行锁续期
//这个方法的作用其实底层也是去执行LUA脚本
RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
//同理去处理Redis续命结果
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", e);
} else {
//如果成功续期,递归继续创建下一个 10S 后的任务
if (res) {
//递归继续创建下一个10S后的任务
RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration();
}
}
});
}
}
}
}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
}
|
从这里我们就知道,获取锁成功就会开启一个定时任务,也就是 watchdog 看门狗,定时任务会定期检查去续期renewExpirationAsync(threadId)。
从这里我们明白,该定时调度每次调用的时间差是 internalLockLeaseTime / 3,也就是 10 秒。
总结
面试的时候简单明了的回答这个问题就是:
只要客户端一旦加锁成功,就会启动一个 watch dog 看门狗,他是一个后台线程,会每隔 10 秒检查一下,如果客户端还持有锁 key,那么就会不断的延长锁 key 的过期时间。
默认情况下,加锁的时间是 30 秒,.如果加锁的业务没有执行完,就会进行一次续期,把锁重置成 30 秒,万一业务的机器宕机了,那就续期不了,30 秒之后锁就解开了。