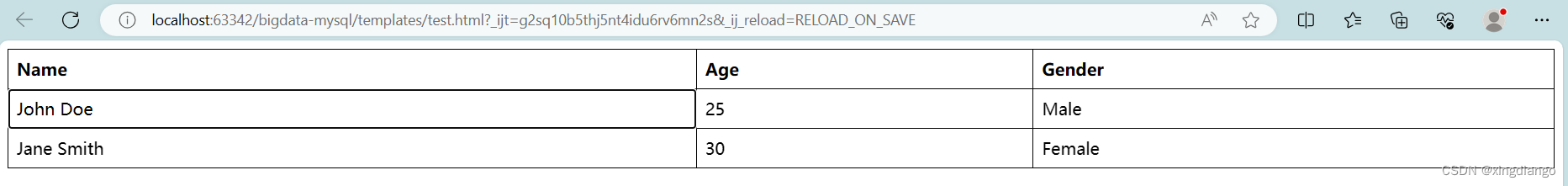
HTML 表格用于在网页上展示数据,通过 <table> 标签及其相关标签来创建。表格由行和列组成,每一行包含一个或多个单元格,单元格可以包含文本、图像、链接等元素。本文将详细介绍 HTML 表格的创建方法、常用标签和属性,以及如何通过 CSS 美化表格。
一、HTML 表格的基本结构
一个简单的 HTML 表格由以下标签组成:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<table>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
- <table>:定义表格的开始和结束。
- <tr>:定义表格中的一行。
- <th>:定义表格的表头单元格,通常用于第一行,表示列的标题。
- <td>:定义表格中的数据单元格,用于存放具体的数据。
二、HTML 表格的常用属性
1. border
border 属性用于设置表格的边框。默认情况下,表格没有边框。
|
1
2
3
|
<table border="1">
<!-- 表格内容 -->
</table>
|
2. cellpadding
cellpadding 属性用于设置单元格内容与单元格边框之间的距离。
|
1
2
3
|
<table border="1" cellpadding="5">
<!-- 表格内容 -->
</table>
|
3. cellspacing
cellspacing 属性用于设置单元格之间的间距。
|
1
2
3
|
<table border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0">
<!-- 表格内容 -->
</table>
|
4. width 和 height
width 和 height 属性用于设置表格的宽度和高度。这些属性可以以像素或百分比为单位设置。
|
1
2
3
|
<table border="1" width="500" height="200">
<!-- 表格内容 -->
</table>
|
三、HTML 表格的高级用法
1. 合并单元格
(1) colspan
colspan 属性用于合并水平方向上的单元格。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th colspan="2">表头 1 和 2 合并</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
(2) rowspan
rowspan 属性用于合并垂直方向上的单元格。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th rowspan="2">表头 1</th>
<td>数据 1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
2. 表格的头部、主体和脚部
(1) <thead>
<thead> 标签用于定义表格的头部,通常包含表头单元格。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<!-- 表格主体 -->
</table>
|
(2) <tbody>
<tbody> 标签用于定义表格的主体,包含数据单元格。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
|
(3) <tfoot>
<tfoot> 标签用于定义表格的脚部,通常用于总结或总计行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td>总计</td>
<td>100</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
|
3. 表格的样式设计
(1) 使用内联样式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<table border="1" style="border-collapse: collapse; width: 500px;">
<tr>
<th style="background-color: #f2f2f2; padding: 8px;">表头 1</th>
<th style="background-color: #f2f2f2; padding: 8px;">表头 2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="padding: 8px; text-align: center;">数据 1</td>
<td style="padding: 8px; text-align: center;">数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="padding: 8px; text-align: center;">数据 3</td>
<td style="padding: 8px; text-align: center;">数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
(2) 使用内部样式表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 500px;
}
th, td {
padding: 8px;
text-align: left;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
th {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
(3) 使用外部样式表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<!-- 在 HTML 文件中 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
<table class="custom-table">
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/* 在 styles.css 文件中 */
.custom-table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 500px;
}
.custom-table th, .custom-table td {
padding: 8px;
text-align: left;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
.custom-table th {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
.custom-table tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
|
4. 响应式表格
在移动设备上,表格可能会超出屏幕宽度,影响用户体验。通过 CSS,可以实现响应式表格,使其在小屏幕上也能良好显示。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
<style>
.responsive-table {
width: 100%;
overflow-x: auto;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
}
th, td {
padding: 8px;
text-align: left;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
th {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
</style>
<div class="responsive-table">
<table>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
<th>表头 3</th>
<th>表头 4</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 5</td>
<td>数据 6</td>
<td>数据 7</td>
<td>数据 8</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
|
四、HTML 表格的完整示例
以下是一个包含多种用法的完整 HTML 表格示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>HTML 表格示例</title>
<style>
.custom-table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
}
.custom-table th, .custom-table td {
padding: 12px;
text-align: left;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
.custom-table th {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
}
.custom-table tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
.custom-table tr:hover {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
.responsive-table {
width: 100%;
overflow-x: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML 表格示例</h1>
<!-- 基本表格 -->
<h2>基本表格</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 合并单元格 -->
<h2>合并单元格</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th colspan="2">表头 1 和 2 合并</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 表格的头部、主体和脚部 -->
<h2>表格的头部、主体和脚部</h2>
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td>总计</td>
<td>100</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
<!-- 响应式表格 -->
<h2>响应式表格</h2>
<div class="responsive-table">
<table class="custom-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>表头 1</th>
<th>表头 2</th>
<th>表头 3</th>
<th>表头 4</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>数据 1</td>
<td>数据 2</td>
<td>数据 3</td>
<td>数据 4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>数据 5</td>
<td>数据 6</td>
<td>数据 7</td>
<td>数据 8</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
五、总结
HTML 表格是网页中展示数据的重要工具。通过 <table>、<tr>、<th>、<td> 等标签,可以创建结构清晰、样式美观的表格。以下是对 HTML 表格相关标签和属性的总结:
table>标签名描述示例<table>定义表格<table><tr>定义表格中的一行<tr><th>定义表格的表头单元格<th><td>定义表格中的数据单元格<td><thead>定义表格的头部<thead><tbody>定义表格的主体<tbody><tfoot>定义表格的脚部<tfoot>
| 属性名 |
描述 |
示例 |
| border |
设置表格的边框 |
<table border="1"> |
| cellpadding |
设置单元格内容与边框之间的距离 |
<table cellpadding="5"> |
| cellspacing |
设置单元格之间的间距 |
<table cellspacing="0"> |
| width |
设置表格的宽度 |
<table width="500"> |
| height |
设置表格的高度 |
<table height="200"> |
| colspan |
合并水平方向上的单元格 |
<th colspan="2"> |
| rowspan |
合并垂直方向上的单元格 |
<th rowspan="2"> |
通过合理使用这些标签和属性,可以创建出结构清晰、样式美观的 HTML 表格,满足各种数据展示的需求。
|