ObjectMapper 忽略字段大小写
核心代码:
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
mapper.configure(MapperFeature.ACCEPT_CASE_INSENSITIVE_PROPERTIES, true);
|
例子:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonMappingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.MapperFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
A a = new A();
a.lastname = "jack";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
mapper.configure(MapperFeature.ACCEPT_CASE_INSENSITIVE_PROPERTIES, true);
A2 convertValue = new A2();
mapper.updateValue(convertValue, a);
System.out.println(convertValue);
} catch (JsonMappingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class A{
String lastname;
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
}
public static class A2{
String lastName;
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "A2 [lastName=" + lastName + "]";
}
}
}
|
ObjectMapper 的一些坑
相信做过Java 开发对这个类应该不陌生,没错,这个类是jackson提供的,主要是用来把对象转换成为一个json字符串返回到前端。
现在大部分数据交换都是以json来传输的,所以这个很重要,那你到底又对这个类有着有多少了解呢,下面我说一下我遇到的一些坑
首先,先把我要说的几个坑需要设置的属性贴出来先
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//反序列化的时候如果多了其他属性,不抛出异常
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
//如果是空对象的时候,不抛异常
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
//取消时间的转化格式,默认是时间戳,可以取消,同时需要设置要表现的时间格式
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))
|
简单说一下这个类的基本用法,以下采用代码块加截图的形式来说明和部分文字件数
package com.shiro.test;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//取消时间的转化格式,默认是时间戳,可以取消,同时需要设置要表现的时间格式
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
objectMapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
//这是最简单的一个例子,把一个对象转换为json字符串
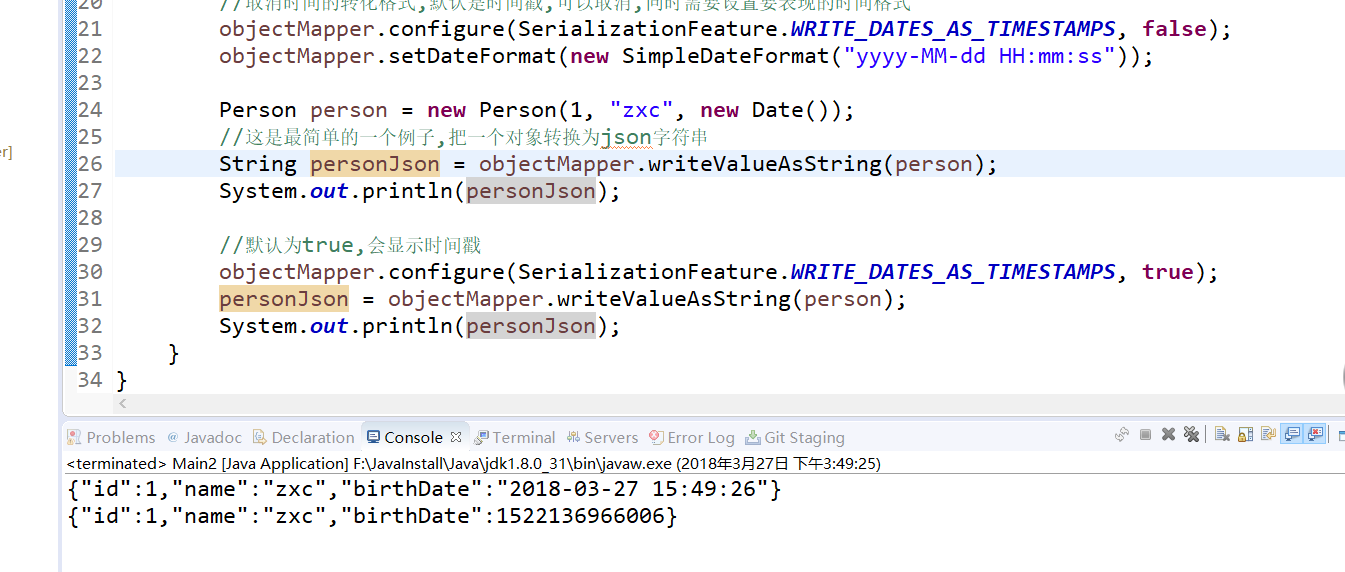
String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
//默认为true,会显示时间戳
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, true);
personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
}
}
|
输出的信息如下
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false)的作用
package com.shiro.test;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
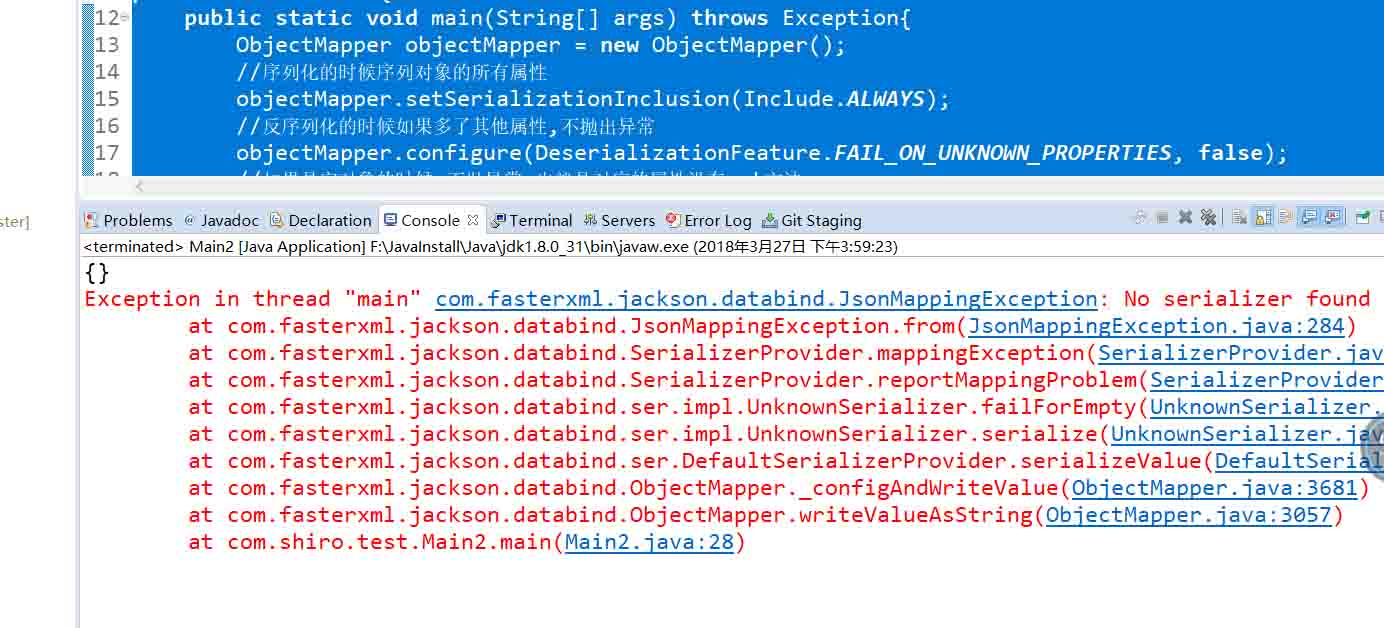
//如果是空对象的时候,不抛异常,也就是对应的属性没有get方法
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
//默认是true,即会抛异常
objectMapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, true);
personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(personJson);
}
}
|
对应的person类此时为
package com.shiro.test;
import java.util.Date;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Date birthDate;
// public Integer getId() {
// return id;
// }
// public void setId(Integer id) {
// this.id = id;
// }
// public String getName() {
// return name;
// }
// public void setName(String name) {
// this.name = name;
// }
// public Date getBirthDate() {
// return birthDate;
// }
// public void setBirthDate(Date birthDate) {
// this.birthDate = birthDate;
// }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", birthDate=" + birthDate + "]";
}
public Person(Integer id, String name, Date birthDate) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birthDate = birthDate;
}
public Person() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
|
结果如下
package com.shiro.test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.ALWAYS);
//反序列化的时候如果多了其他属性,不抛出异常
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
// Person person = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
// String personJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person);
// System.out.println(personJson);
//注意,age属性是不存在在person对象中的
String personStr = "{"id":1,"name":"zxc","age":"zxc"}";
Person person = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
//默认为true
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, true);
person = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
|
执行后的结果如下
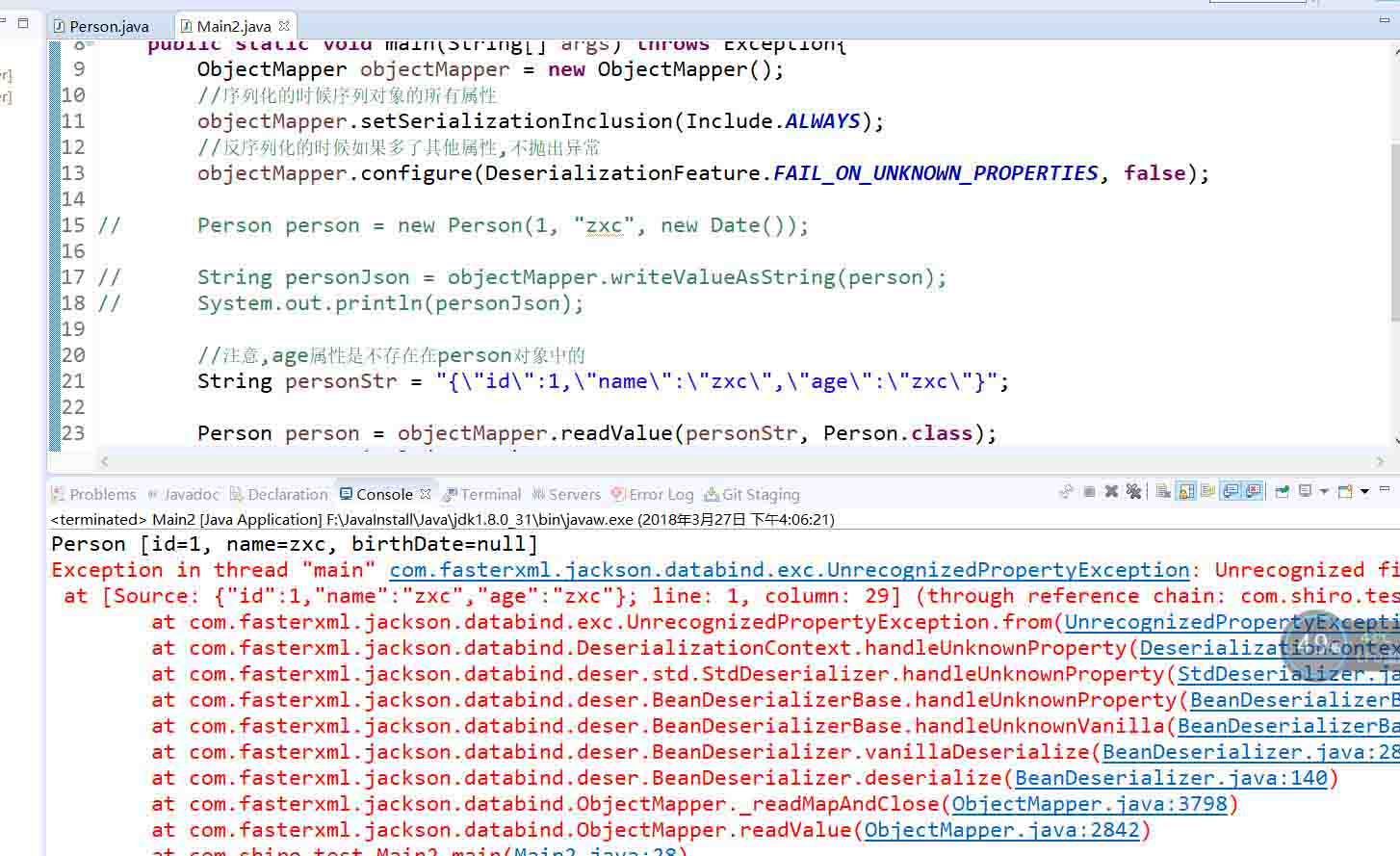
这些便是这几个属性的作用所以,由于第一个比较简单我就这样说一下吧
Include.ALWAYS 是序列化对像所有属性
Include.NON_NULL 只有不为null的字段才被序列化
Include.NON_EMPTY 如果为null或者 空字符串和空集合都不会被序列化
然后再说一下如何把一个对象集合转换为一个 Java里面的数组
package com.shiro.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//序列化的时候序列对象的所有属性
objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.NON_DEFAULT);
Person person1 = new Person(1, "zxc", new Date());
Person person2 = new Person(2, "ldh", new Date());
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>();
persons.add(person1);
persons.add(person2);
//先转换为json字符串
String personStr = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(persons);
//反序列化为List<user> 集合,1需要通过 TypeReference 来具体传递值
List<Person> persons2 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, new TypeReference<List<Person>>() {});
for(Person person : persons2) {
System.out.println(person);
}
//2,通过 JavaType 来进行处理返回
JavaType javaType = objectMapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, Person.class);
List<Person> persons3 = objectMapper.readValue(personStr, javaType);
for(Person person : persons3) {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
}
|
|