SpringBoot怎么解析应用参数args
前文深入解析了SpringBoot启动的开始阶段,包括获取和启动应用启动监听器、事件与广播机制,以及如何通过匹配监听器实现启动过程各阶段的自定义逻辑。接下来,我们将探讨SpringBoot启动类
|
前文深入解析了SpringBoot启动的开始阶段,包括获取和启动应用启动监听器、事件与广播机制,以及如何通过匹配监听器实现启动过程各阶段的自定义逻辑。接下来,我们将探讨SpringBoot启动类main函数中的参数args的作用及其解析过程。
一、入口将main方法的参数args封装成一个对象DefaultApplicationArguments,以便方便地解析和访问启动参数
二、默认应用程序参数DefaultApplicationArguments1、功能概述DefaultApplicationArguments是SpringBoot中的一个类,用于处理启动时传入的参数。它实现了ApplicationArguments接口,并提供了一些便捷的方法来访问传入的命令行参数和选项参数。
2、使用示例假设我们在命令行中运行应用,传递了一些参数
在代码中,我们可以使用DefaultApplicationArguments来解析这些参数
3、接口ApplicationArgumentsApplicationArguments是DefaultApplicationArguments类的父接口
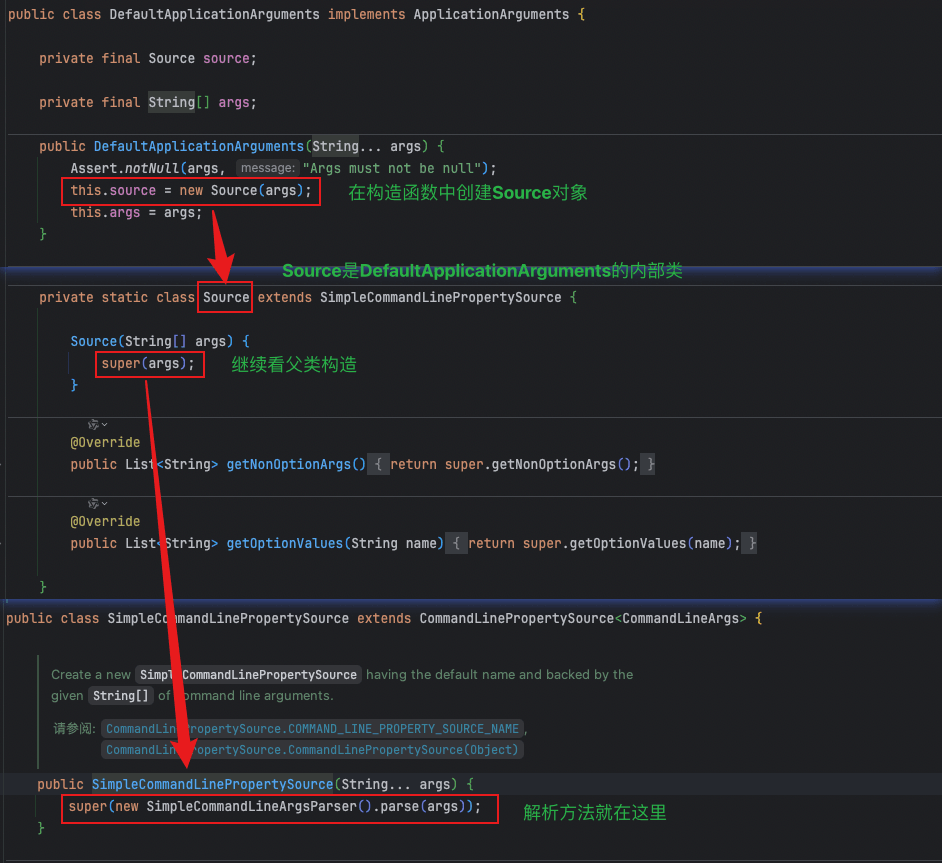
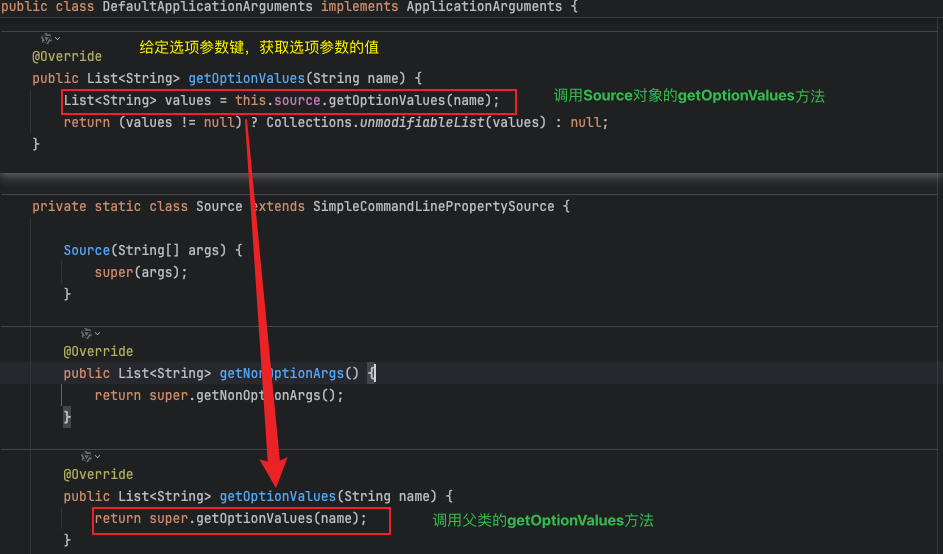
4、实现类DefaultApplicationArguments代码很简单,对外暴露使用DefaultApplicationArguments,内部实现都在Source中
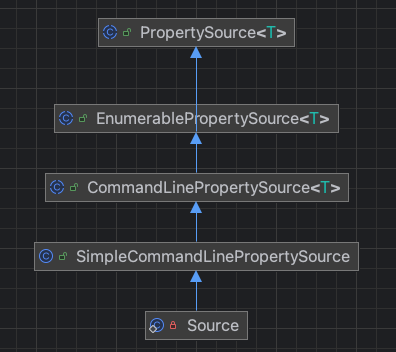
三、SourceSource是DefaultApplicationArguments解析参数内部的真正实现类,类图如下,逐一分析。
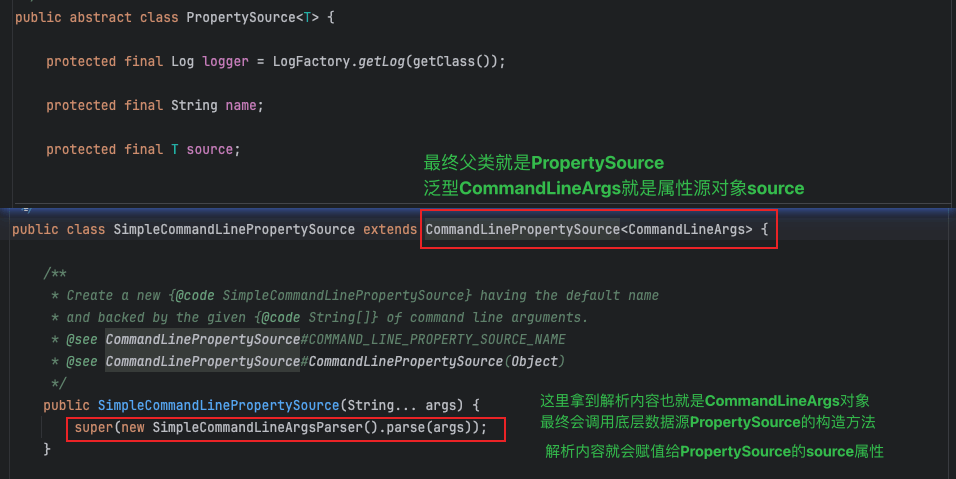
1、属性源PropertySource PropertySource是Spring框架中的一个核心抽象类,用于表示属性(键值对)的来源。通过将各种配置来源(如系统属性、环境变量、配置文件等)封装为PropertySource对象,Spring可以提供统一的接口来读取和管理这些配置数据。
2、枚举属性源EnumerablePropertySource EnumerablePropertySource继承自PropertySource,主要用于定义getPropertyNames()方法,可以获取属性源对象中所有属性键的名称。
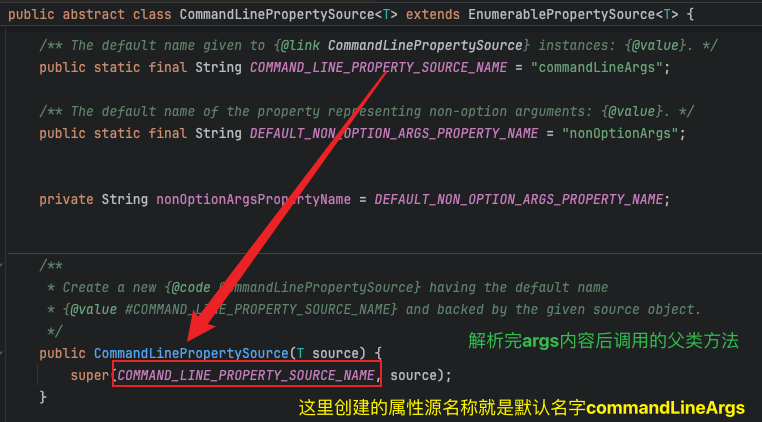
3、命令行属性源CommandLinePropertySource CommandLinePropertySource是Spring框架中用于处理命令行参数的PropertySource实现。它可以将应用程序启动时传入的命令行参数解析成键值对,便于在应用配置中使用。
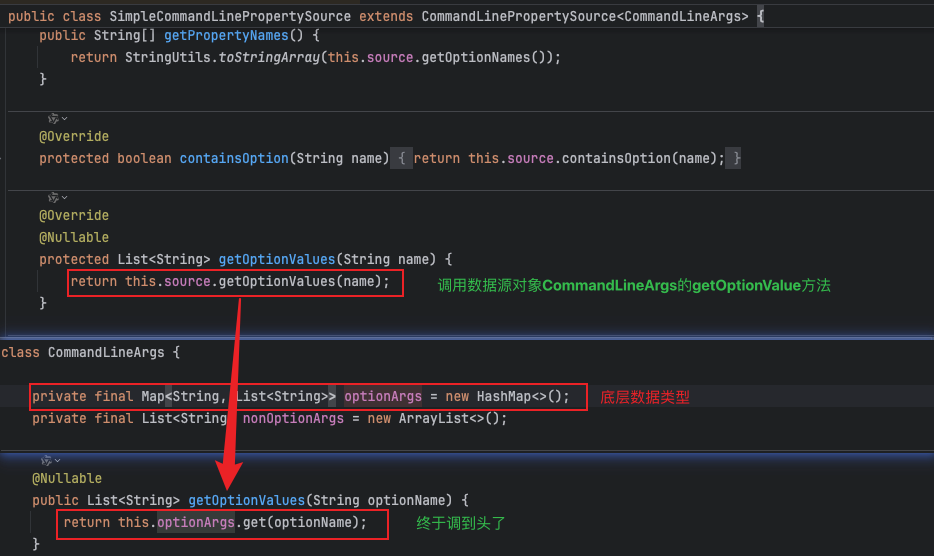
4、简单命令行属性源SimpleCommandLinePropertySource SimpleCommandLinePropertySource是Spring框架中的一个类,继承自CommandLinePropertySource,用于解析和处理命令行参数。它设计为简单易用,通过接收一个字符串数组(即命令行参数 args),将参数分为"选项参数"和"非选项参数"两类。
四、解析参数原理在上一节中,我们了解了应用程序参数args被解析后的结构和存储方式。接下来,我们回到文章开头,详细解析参数是如何被逐步解析出来的。
根据new DefaultApplicationArguments(args)寻找解析arg的位置
解析完arg调用父类CommandLinePropertySource的构造方法
1、解析方法SimpleCommandLineArgsParser通过遍历传入的命令行参数数组,根据参数的格式,将参数解析并分为选项参数和非选项参数。
属性源对象类型CommandLineArgs
2、解析参数的存储和访问解析方法很简单,所有内容都在SimpleCommandLineArgsParser的parse方法中完成。相比之下,存储和访问方式更为复杂。 存储位置位于属性源对象PropertySource中。从代码可知,args表示命令行参数,因此属性源名称为命令行属性源默认名称commandLineArgs,属性源对象为解析args后的键值对。
访问查询方式的底层实现就是操作CommandLineArgs中的optionArgs(选项参数)和nonOptionArgs(非选项参数)两个集合,但此过程经过多次跳转,最终依次通过 DefaultApplicationArguments -> DefaultApplicationArguments#Source -> SimpleCommandLinePropertySource -> CommandLineArgs获取,其中CommandLineArgs就是是命令行属性源对象。这种设计主要是为了提供更灵活、安全的访问方式,避免直接暴露内部数据结构带来的潜在风险。
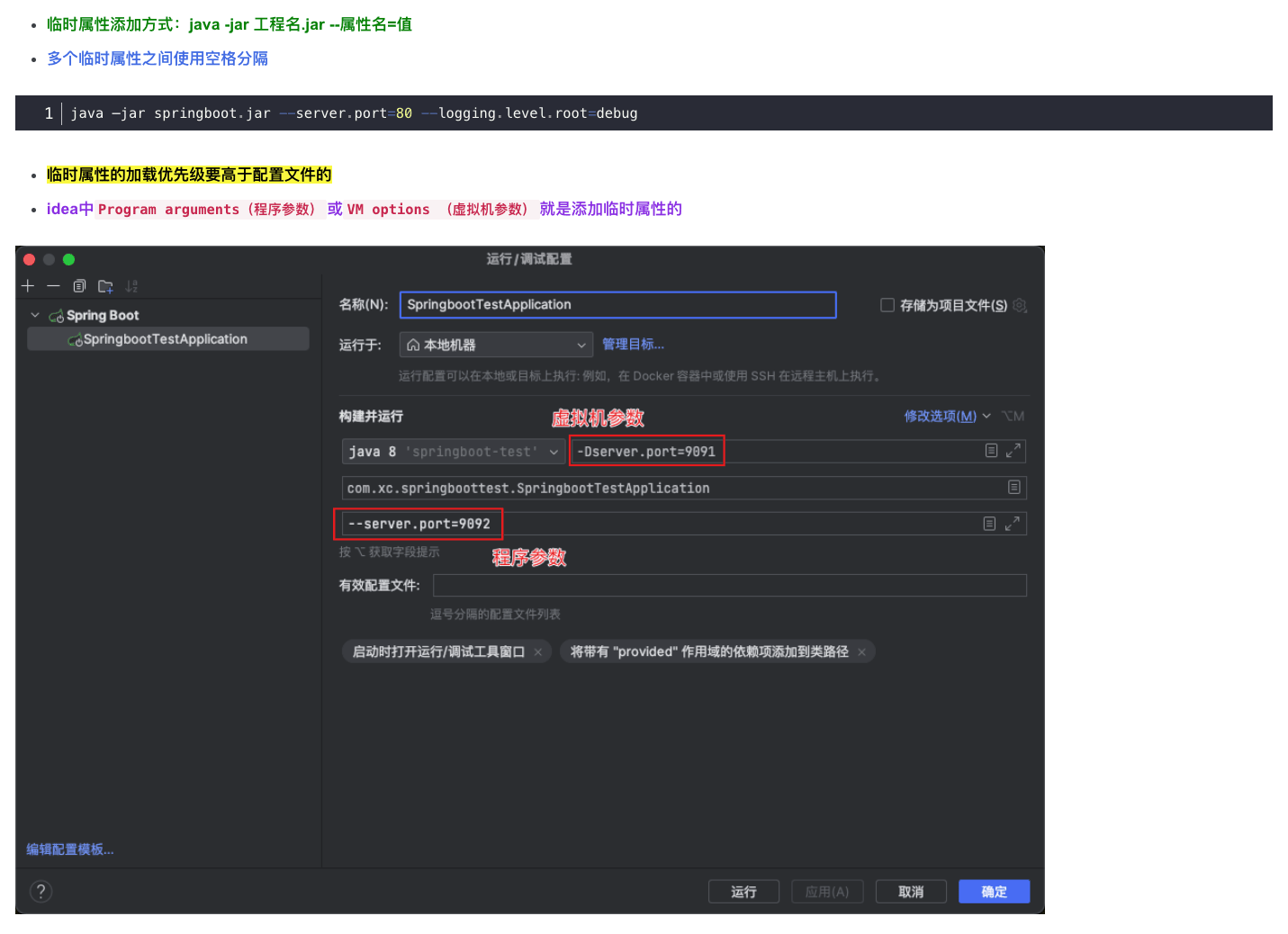
3、实际应用之前在SpringBoot基础(二):配置文件详解文章中有介绍过配置文件设置临时属性,这次回过头再来看,就很清晰明了了。
总结
|
您可能感兴趣的文章 :
-
MybatisPlus中saveBatch方法的使用介绍
1.MyBatis PlussaveBatch 方法 使用及简介 MyBatis Plus 是 Java 生态中一款流行的库,它扩展了 MyBatis 的功能,MyBatis 是一个简化 Java 应用中数据库操作 -
springboot3.x版本集成log4j冲突以及解决log4j冲突不生
springboot3.x版本集成log4j冲突及log4j冲突不生效 由于springboot自带的日志logback会与log4j冲突,因此在网上搜了之后,进行了去除操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 -
使用mybatis log plugin插件展示出数据库查询语句方
1、安装mybatis log plugin插件 直接插件市场搜该插件进行安装就行,安装完成后,会有如下图标 2、需要集成log4j springboot版本需要集成log4j,集 -
若依后端MyBatis改为MyBatis-Plus方式
1.引入MyBatis-Plus依赖 在总目录的pom.xml,导入依赖 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 mybatis-plus.version3.4.3/mybatis-plus.version !-- mybatis-plus 增强CRUD -- dependency groupIdcom. -
SpringSecurity+jwt+captcha登录认证授权流程总结
SpringSecurity+jwt+captcha登录认证授权总结 版本信息: springboot 3.2.0、springSecurity 6.2.0、mybatis-plus 3.5.5 认证授权思路和流程: 未携带token,访问登 -
SpringBoot怎么使用过滤器进行XSS防御
在Spring Boot中,我们可以使用注解的方式来进行XSS防御。注解是一种轻量级的防御手段,它可以在方法或字段级别对输入进行校验,从而防止 -
idea中文件被Mark as Plain Text后恢复方式
idea文件被Mark as Plain Text后恢复 1、idea中文件被标记:Mark as Plain Text 在idea中不小心把文件进行Mark as Plain Text标记后,会变成纯文本 如下图所示
-
Java对象创建的过程及内存布局的介绍
2021-06-05
-
Java基础学习之集合底层原理的介绍
2021-05-27
-
java实现PDF转HTML文档的示例代码
2021-05-26
-
记录Java Log的几种方式
2021-06-05
-
springboot整合RabbitMQ发送短信的实现
2021-05-16