Java8 CompletableFuture异步编程解读介绍
CompletableFuturede介绍 Java 8 引入了 CompletableFuture 类,这是 Java 异步编程的一个重要进展。 CompletableFuture 提供了一种基于未来结果的异步编程模型,允许你以更加直观和易于理解的方式编写非阻塞
CompletableFuturede介绍Java 8 引入了 CompletableFuture 类,这是 Java 异步编程的一个重要进展。 CompletableFuture 提供了一种基于未来结果的异步编程模型,允许你以更加直观和易于理解的方式编写非阻塞代码。 CompletableFuturede使用场景CompletableFuture 主要用于:
常用异步编程实现方案- Thread特点:
使用示例:
- ExecutorService特点:
使用示例: 有返回值:
无返回值:
- CountDownLatch特点:
使用示例:
- CyclicBarrier特点:
使用示例:
- ForkJoinPool特点:
使用示例:
- CompletableFuture特点:
使用示例:
各种实现方案总结
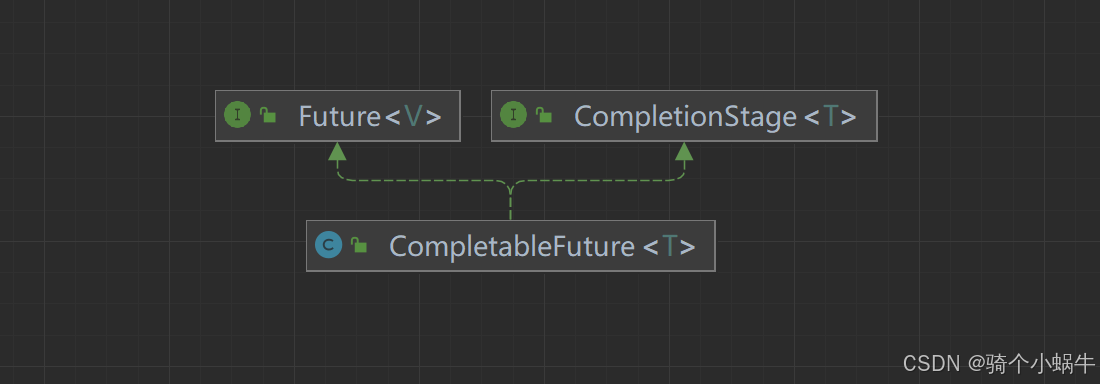
CompletableFuturede结构
CompletableFuture实现了Future接口和CompletionStage接口。 结构梳理
- Future接口Future接口是JDK 5引入的,该接口属于java.util.concurrent包。 Future接口的目的是表示异步计算的结果,它允许你提交一个任务给一个 Executor(执行器),并在稍后获取任务的结果。 主要方法:
- CompletionStage接口CompletionStage 接口是 Java 8 引入的一个重要接口,用于描述异步计算的生命周期和结果。 CompletionStage 提供了一套方法,用于处理异步计算的结果、组合多个计算、处理异常等。 主要方法:
常用方法
CompletableFuture使用示例1. 基本异步操作CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() 和 CompletableFuture.runAsync() 是最常用的启动异步任务的方法。
2. 任务链式调用通过 thenApply(), thenAccept(), thenRun() 等方法,可以将多个异步任务串联在一起。
3. 多个异步任务组合使用 thenCombine()、thenCompose()、allOf() 和 anyOf() 等方法可以组合多个异步任务,执行复杂的操作。
示例1:组合两个异步任务
示例2:使用 allOf() 等待多个任务完成
4. 异常处理在异步任务中,异常可能会发生。CompletableFuture 提供了 exceptionally() 和 handle() 方法来处理异常。
5. 并行执行多个任务使用 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync() 或 runAsync() 来并行执行多个任务,然后使用 allOf() 或 anyOf() 等方法等待这些任务的完成。
6. 处理返回值的转换通过 thenApply() 等方法可以对异步任务的结果进行转换处理。
|
您可能感兴趣的文章 :
-
Java使用JNA调用DLL文件
1、什么是JNA? JNA(Java Native Access)是一个在 Java 中调用本地代码的开源框架,提供了一种简单、高效的方式来访问本地动态链接库(如.d -
Java8 CompletableFuture异步编程解读介绍
CompletableFuturede介绍 Java 8 引入了 CompletableFuture 类,这是 Java 异步编程的一个重要进展。 CompletableFuture 提供了一种基于未来结果的异步编程模 -
基于Maven pom文件使用分析
project Maven 是一个强大的构建和依赖管理工具,pom.xml 文件是 Maven 项目的核心配置文件,用于定义项目的构建、依赖关系、插件、目标等。它 -
Java-URLDecoder、URLEncoder使用及说明介绍
前言 Java中的URLDecoder和URLEncoder是用于对URL进行编码和解码的类。 URL编码是将URL中的特殊字符转换成特定的格式,以便于在URL中传递参数。 -
SpringBoot内置Tomcat启动方式
一、Tomcat相关配置类如何加载的? 在springboot项目中,我们只需要引入spring-boot-starter-web依赖,启动服务成功,我们一个web服务就搭建好了, -
Springboot接收Get参数实践过程
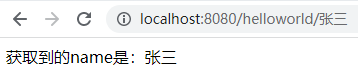
一、参数直接在路径中 1.假设请求地址是如下这种 RESTful 风格 hangge 这个参数值直接放在路径里面: http://localhost:8080/helloworld/张三 1 2 3 4 5 -
MyBatis中的N+1问题的解决方法
N+1 问题是指在进行一对多查询时,应用程序首先执行一条查询语句获取结果集(即 +1),然后针对每一条结果,再执行 N 条额外的查询语句 -
MyBatis中 #{} 和 ${} 的区别介绍
在MyBatis中,#{}和${}是两种常见的占位符,它们的作用和使用场景有所不同。理解它们的区别对于正确使用MyBatis非常重要。 在Mybatis面试中常 -
MyBatis实现CRUD的代码
准备工作 创建module(Maven的普通Java模块):mybatis-002-crud pom.xml 打包方式jar 依赖: mybatis依赖 mysql驱动依赖 junit依赖 logback依赖 mybatis-config
-
Java对象创建的过程及内存布局的介绍
2021-06-05
-
Java基础学习之集合底层原理的介绍
2021-05-27
-
java实现PDF转HTML文档的示例代码
2021-05-26
-
记录Java Log的几种方式
2021-06-05
-
springboot整合RabbitMQ发送短信的实现
2021-05-16