前端状态管理出现的意义及解决的问题
随着前端应用的逐步复杂,我们的组件中需要使用越来越多的状态。有的时候我们需要使用子组件将状态传递给父组件就会比较复杂,数据的向上传递过程我们可能会使用回调函数或是数据绑定的形式去处理,就会让代码晦涩难懂。
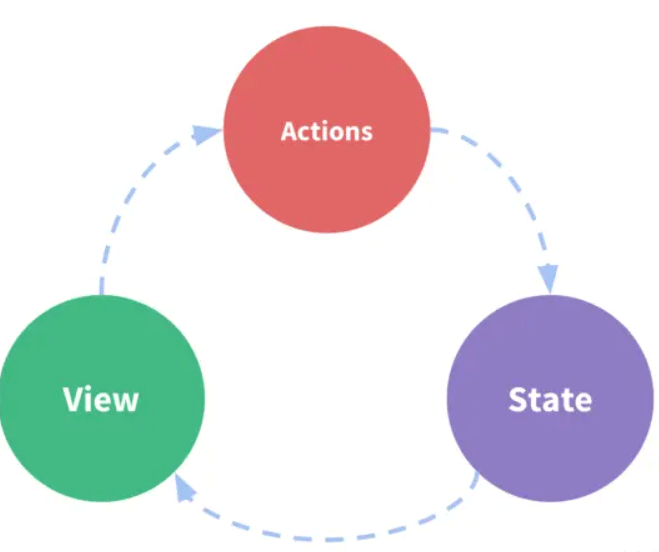
我们需要一种方式,能够让数据在所有组件中共享,同时能以简单的方式进行传递,这种组织数据的方式就是状态管理。我们很自然的就想到,把数据放到所有需要使用的组件的公共祖先上,在使用时自上而下传递即可。
在 vue.js 中,我们主要说的状态管理库就是 vuex,当然,只要你能实现有条理的组织数据,那么它都可以认为是一种状态管理库。
事实上,我们可以简单的这样理解【状态管理】这个词,vuex 实际上做的事情就是:
- 在顶层实现一个数据管理的仓库 store,将所有组件间需要共享的数据放置于此;
- 同时组件也可以对这个 store 内的数据进行更新,同时更新完之后响应式更新所有使用此数据组件的视图;

Vuex 源码解读
Vuex 公共方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
export function find(list, f) {
return list.filter(f)[0];
}
export function deepCopy(obj, cache = []) {
if (obj === null || typeof obj !== 'object') {
return obj;
}
const hit = find(cache, c => c.original === obj);
if (hit) {
return hit.copy;
}
const copy = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
cache.push({
original: obj,
copy,
});
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
copy[key] = deepCopy(obj[key], cache);
});
return copy;
}
export function forEachValue(obj, fn) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => fn(obj[key], key));
}
export function isObject(obj) {
return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object';
}
export function isPromise(val) {
return val && typeof val.then === 'function';
}
export function assert(condition, msg) {
if (!condition) throw new Error(`[vuex] ${msg}`);
}
export function partial(fn, arg) {
return function () {
return fn(arg);
};
}
|
Vuex 介绍及深入使用
在说 vuex 之前,我们必须说一说 flux 架构,flux 架构可谓是状态管理的鼻祖。
flux 架构最早由 facebook 推出,主要是为了处理当时他们的 react 框架下状态管理的问题,但在当时来讲,整个设计比较复杂,后来人们简化了其中的一些理念,但是保留了核心思想,继而依据框架实现了很多不同的状态管理库,例如 redux,vuex 等等。其中 redux 大多数被用在了 react 项目中,而 vuex 就是在 vue 框架中实现的这么一个 flux 架构的状态管理库。
**flux 架构约定,存放数据的地方称为 store,store 内部的 state 是数据本身,我们必须通过 action 才能修改 store 里的 state。**这里的 action 指的意思是 行为,在大部分实现里面是一个函数,通过调用函数来更改 store 内部的 state。
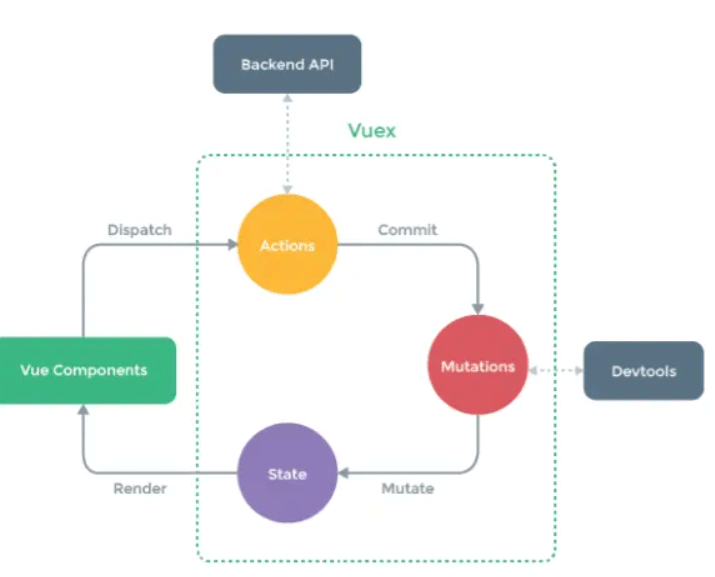
vuex 中,我们可以通过 mutation 来【同步】的改变 state,这时候就可以在组件中通过 commit 进行调用更改 state。
同样的,我们也可以通过 action 来【异步】更改 state,不过在 action 中,我们还是需要调用 mutation。
Vuex 使用(官网)
网址链接:vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/st…
1、基本框架
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {},
});
|
2、基本使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
},
mutations: {
increment(state, payload = 1) {
state.count += payload;
},
},
actions: {},
modules: {},
});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<template>
<div class="home">
<div>count: {{ count }}</div>
<button @click="increment">增加</button>
<button @class="decrement">减少</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
},
},
methods: {
increment() {
// 使用 commit 派发 mutation 事件
// this.$store.commit("increment");
// 可以传递参数
this.$store.commit('increment', 2);
},
decrement() {},
},
};
</script>
|
3、State
可以使用计算属性获取 state 中的数据:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
|
3.1 mapState 辅助函数
当一个组件需要获取多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用 mapState 辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
import { mapState } from "vuex";
computed: {
...mapState(["num"])
}
|
4、Getter
Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义 getter(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: 'foo', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: 'bar', done: false },
],
},
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done);
},
},
});
|
4.1 通过属性访问
Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,你可以以属性的形式访问这些值:
|
1
|
store.getters.doneTodos; // -> [{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true }]
|
Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
getters: {
// ...
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length;
};
}
|
4.2 通过方法访问
你也可以通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
getters: {
// ...
getTodoById: state => id => {
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id);
};
}
|
|
1
|
store.getters.getTodoById(2); // -> { id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
|
【注意】:getter 在通过方法访问时,每次都会去进行调用,而不会缓存结果。
4.3 mapGetters 辅助函数
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters(['doneTodosCount', 'anotherGetter']),
},
};
|
如果你想将一个 getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式:
|
1
2
3
4
|
...mapGetters({
// 把 this.doneCount 映射为 this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
|
5、Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1,
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++;
},
},
});
|
你不能直接调用一个 mutation handler。这个选项更像是事件注册:“当触发一个类型为 increment 的 mutation 时,调用此函数。”要唤醒一个 mutation handler,你需要以相应的 type 调用 store.commit 方法:
|
1
|
store.commit('increment');
|
5.1 提交载荷(Payload)
你可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
mutations: {
increment (state, n) {
state.count += n
}
}
// 使用方法
store.commit('increment', 10)
|
在大多数情况下,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
// 使用方法
store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
|
对象风格的提交方式:
提交 mutation 的另一种方式是直接使用包含 type 属性的对象:
|
1
2
3
4
|
store.commit({
type: 'increment',
amount: 10,
});
|
当使用对象风格的提交方式,整个对象都作为载荷传给 mutation 函数,因此 handler 保持不变:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
|
5.2 使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
使用常量替代 mutation 事件类型在各种 Flux 实现中是很常见的模式。这样可以使 linter 之类的工具发挥作用,同时把这些常量放在单独的文件中可以让你的代码合作者对整个 app 包含的 mutation 一目了然:
|
1
2
|
// mutation-types.js
export const SOME_MUTATION = 'SOME_MUTATION';
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
// store.js
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { ... },
mutations: {
// 我们可以使用 ES2015 风格的计算属性命名功能来使用一个常量作为函数名
[SOME_MUTATION] (state) {
// mutate state
}
}
})
|
5.3 Mutation 必须是同步函数
一条重要的原则就是要记住 mutation 必须是同步函数。为什么?请参考下面的例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mutations: {
someMutation (state) {
api.callAsyncMethod(() => {
state.count++
})
}
}
|
现在想象,我们正在 debug 一个 app 并且观察 devtool 中的 mutation 日志。每一条 mutation 被记录,devtools 都需要捕捉到前一状态和后一状态的快照。然而,在上面的例子中 mutation 中的异步函数中的回调让这不可能完成:因为当 mutation 触发的时候,回调函数还没有被调用,devtools 不知道什么时候回调函数实际上被调用 —— 实质上任何在回调函数中进行的状态的改变都是不可追踪的。
5.4 在组件中提交 Mutation
你可以在组件中使用 this.$store.commit('xxx') 提交 mutation,或者使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy', // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment', // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
}),
},
};
|
6、Action
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
让我们来注册一个简单的 action:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
},
actions: {
increment(context) {
context.commit('increment');
},
},
});
|
Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。当我们在之后介绍到 Modules 时,你就知道 context 对象为什么不是 store 实例本身了。
实践中,我们会经常用到 ES2015 的参数解构来简化代码(特别是我们需要调用 commit 很多次的时候):
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
actions: {
increment ({ commit, state, getters }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
|
7、分发 Action
Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发:
|
1
|
store.dispatch('increment');
|
乍一眼看上去感觉多此一举,我们直接分发 mutation 岂不更方便?实际上并非如此,还记得 mutation 必须同步执行这个限制么?Action 就不受约束!我们可以在 action 内部执行异步操作:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
actions: {
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}
|
Actions 支持同样的载荷方式和对象方式进行分发:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10,
});
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10,
});
|
7.1 在组件中分发 Action
你在组件中使用 this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用(需要先在根节点注入 store):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import { mapActions } from 'vuex';
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy', // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment', // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
}),
},
};
|
7.2 组合 Action
Action 通常是 异步 的,那么如何知道 action 什么时候结束呢?更重要的是,我们如何才能组合多个 action,以处理更加复杂的异步流程?
首先,你需要明白 store.dispatch 可以处理被触发的 action 的处理函数返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍旧返回 Promise:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
actions: {
actionA ({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('someMutation')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
}
|
现在你可以:
|
1
2
3
|
store.dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
// ...
});
|
在另外一个 action 中也可以:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
actions: {
// ...
actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
return dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
commit('someOtherMutation')
})
}
}
|
最后,如果我们利用 async / await,我们可以如下组合 action:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// 假设 getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}
|
一个 store.dispatch 在不同模块中可以触发多个 action 函数。在这种情况下,只有当所有触发函数完成后,返回的 Promise 才会执行。
8、严格模式
开启严格模式,仅需在创建 store 的时候传入 strict: true:
|
1
2
3
4
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
strict: true,
});
|
在严格模式下,无论何时发生了状态变更且不是由 mutation 函数引起的,将会抛出错误(但是数据还是会改变)。这能保证所有的状态变更都能被调试工具跟踪到。
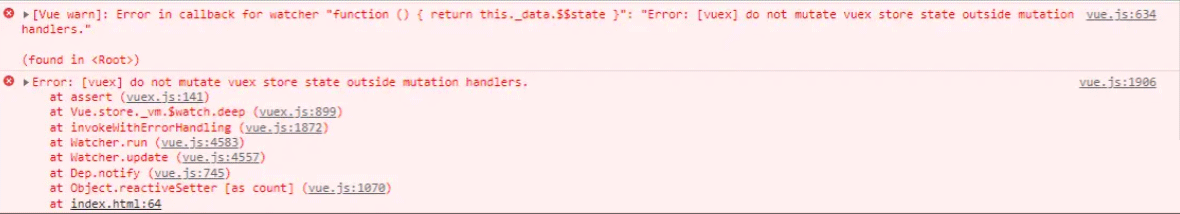
8.1 开发环境与发布环境
不要在发布环境下启用严格模式! 严格模式会深度监测状态树来检测不合规的状态变更 —— 请确保在发布环境下关闭严格模式,以避免性能损失。
类似于插件,我们可以让构建工具来处理这种情况:
|
1
2
3
4
|
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
});
|
vue.js 服务端渲染介绍
大多数我们使用的 UI 框架如 vue 和 react,都是在客户端进行渲染,也就是说每个用户在加载进来我们所有的 html 文件和 js 文件之后,才开始渲染页面的内容。
但是这样做会有两个问题,一个是如果用户网络速度比较慢,如果我们渲染的内容比较多的话,就会产生一个延迟,造成不好的用户体验。另一个是某些爬虫,例如百度的搜索收录的爬虫,在爬取你的页面时,获取不到你的页面的真实内容,导致站点 SEO 权重变低。
所以很多需要 SEO 的页面,都需要在服务端提前渲染好 html 的内容,在用户访问时先返回给用户内容,这杨对用户和爬虫都非常友好。
我们可以通过直接在页面上右击查看网页源代码,来查看一个页面是否有服务端渲染。
1、客户端渲染和服务端渲染
客户端渲染
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>客户端渲染</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
document.body.innerHTML = '<div>你好</div>';
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
在 Network 的中 Preview 中无数据,在 Response 中的没有 DOM 标签:
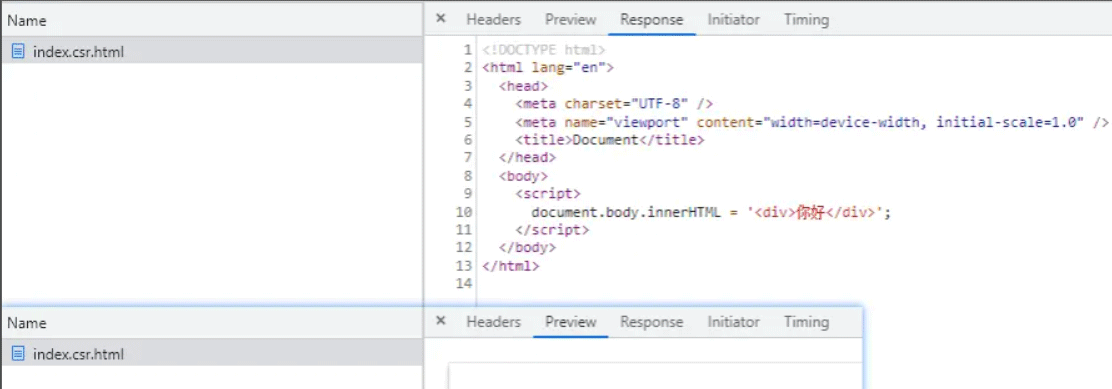
查看网页源代码:

2、服务端渲染
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>服务端渲染</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>你好</div>
</body>
</html>
|
在 Network 的中 Preview 中有数据,在 Response 中的有 DOM 标签:
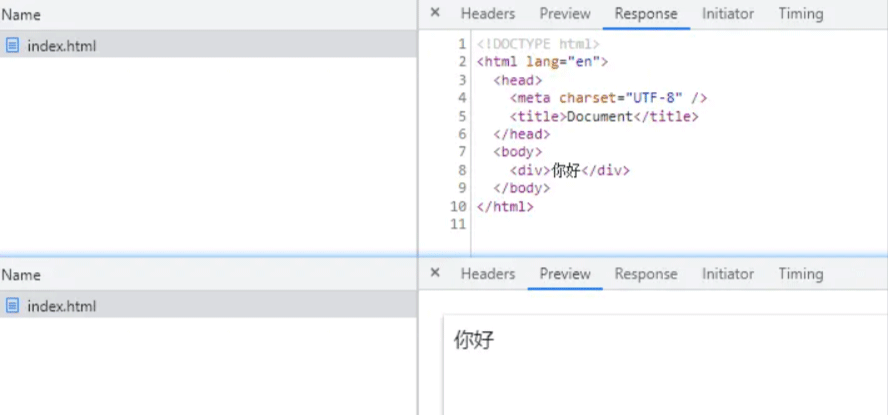
查看网页源代码:
客户端路由
在控制台中可以看到,切换路由的时候并没有发起 ajax 请求。
3、服务端渲染实例
vue.js 的服务端渲染非常简单,我们只需要在 node.js 中通过 vue-server-renderer 模块,调用对应服务端渲染的渲染器对组件渲染即可,他就会生成组件对应的 html 内容。渲染成功的 html 标签,我们可以直接返回到客户端作为初始请求 html 的返回值。
|
1
|
yarn add express vue vue-server-renderer
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
const Vue = require('vue');
const createRenderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer;
const vm = new Vue({
data() {
return {
count: 100,
};
},
template: `<div>{{ count }}</div>`,
});
const renderer = createRenderer();
renderer.renderToString(vm, (err, html) => {
console.log('html ==========', html); // <div data-server-rendered="true">100</div>
});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
const Vue = require('vue');
const createRenderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer;
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
// ! 服务端路由
app.get('*', function (req, res) {
const vm = new Vue({
data() {
return {
url: `服务端路由 ${req.url}`,
count: 100,
};
},
template: `<div>{{ url }} - {{ count }}</div>`,
});
const renderer = createRenderer({
// 设置模板
template: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, './index.template.html'), 'utf-8'),
});
renderer.renderToString(vm, (err, html) => {
res.send(html);
});
});
const PORT = 8080;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`服务器启动在 ${PORT} 端口`);
});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>服务端渲染Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>这里是模板</h1>
<!--! 中间不能带空格 -->
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</body>
</html>
|
- 执行 index.js 文件:node ./index.js
我们需要注意的一点是,在服务端渲染组件,我们使用不了 window、location 等浏览器环境中的对象,所以如果组件内部使用了这种内容会报错。
同时,在服务端渲染时我们要注意,组件的生命周期也会只执行 beforeCreate 和 created 这两个,所以在此声明周期里面不能使用 window,但是可以在其他声明周期比如 mounted 中使用。还有渲染的数据,对于服务端渲染的组件来说,我们不应该发请求获取组件数据,而是应该直接渲染时使用数据进行渲染。
路由也是如此,在 vue 客户端使用路由的时候,我们也需要在服务端对路由进行匹配,从而得知具体需要渲染的组件是哪个。
3、同构 - 客户端渲染和服务端渲染
参考文档(Vue 文档中 - Vue 服务端渲染):ssr.vuejs.org/zh/
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
/*
客户端 webpack 配置
*/
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/entry-client.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist'),
publicPath: '/dist/',
filename: 'build.js',
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
},
],
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['*', '.js', '.vue'],
},
};
|
- ./webpack.server.config.js
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/*
服务端 webpack 配置
*/
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.config');
const config = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
target: 'node',
entry: {
app: './src/entry-server.js',
},
output: {
path: __dirname,
filename: 'server.bundle.js',
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2',
},
});
console.log('config ============ ', config);
module.exports = config;
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
{
"name": "06",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "webpack.config.js",
"dependencies": {
"babel-core": "^6.26.3",
"babel-loader": "^7.1.5",
"babel-preset-env": "^1.7.0",
"babel-preset-stage-3": "^6.24.1",
"express": "^4.17.1",
"vue": "^2.6.11",
"vue-router": "^3.3.2",
"vue-server-renderer": "^2.6.11",
"vuex": "^3.4.0",
"webpack": "^3.12.0",
"webpack-merge": "^4.2.2"
},
"devDependencies": {
"vue-loader": "^13.7.3",
"vue-template-compiler": "^2.6.11"
},
"scripts": {
"build-server": "webpack --config webpack.server.config.js",
"build-client": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<template>
<div>
<h1>this is App.vue</h1>
<router-link to="/">root</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">about</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
|
|
1
2
3
|
<template>
<div>Home {{ $store.state.timestamp }}</div>
</template>
|
|
1
2
3
|
<template>
<div>about {{ $store.state.timestamp }}</div>
</template>
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
/*
entry-client 和 entry-server 共同的文件
*/
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Home from './Home';
import About from './About';
import App from './App';
Vue.use(Router);
Vue.use(Vuex);
export function createApp() {
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
timestamp: new Date().getTime(),
},
});
if (typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.store) {
store.replaceState(window.store);
}
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
],
});
const vm = new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App),
});
return { vm, router, store };
}
|
- ./src/entry-server.js 第一种
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
/*
服务端渲染 - 入口
*/
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer();
const { createApp } = require('./index');
const app = express();
app.use('/dist', express.static(path.join(__dirname, './dist')));
app.get('/build.js', function (req, res) {
const pathUrl = path.resolve(process.cwd(), './dist/build.js');
console.log(pathUrl);
res.sendFile(pathUrl);
});
app.get('*', function (req, res) {
const url = req.url;
const { vm, router } = createApp();
router.push(url);
/*
const matchedComponents: Array<Component> = router.getMatchedComponents(location?)
返回目标位置或是当前路由匹配的组件数组 (是数组的定义/构造类,不是实例)。通常在服务端渲染的数据预加载时使用。
*/
const matchedComponent = router.getMatchedComponents();
if (!matchedComponent) {
// 404 处理
} else {
renderer.renderToString(vm, function (err, html) {
res.send(html);
});
}
});
const PORT = 8080;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`服务器启动在 ${PORT} 端口`);
});
/*
此时可以执行 yarn build-server 编译 entry-server 文件,生成 server.bundle.js
执行 node ./server.bundle.js 查看服务端路由的结果
*/
|
- ./src/entry-server.js 第二种
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
/*
服务端渲染 - 入口
*/
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer({
template: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(process.cwd(), './index.template.html'), 'utf-8'),
});
const { createApp } = require('./index');
const app = express();
app.use('/dist', express.static(path.join(__dirname, './dist')));
app.get('/build.js', function (req, res) {
const pathUrl = path.resolve(process.cwd(), './dist/build.js');
console.log(pathUrl);
res.sendFile(pathUrl);
});
app.get('*', function (req, res) {
const url = req.url;
const { vm, router, store } = createApp();
router.push(url);
/*
const matchedComponents: Array<Component> = router.getMatchedComponents(location?)
返回目标位置或是当前路由匹配的组件数组 (是数组的定义/构造类,不是实例)。通常在服务端渲染的数据预加载时使用。
*/
const matchedComponent = router.getMatchedComponents();
if (!matchedComponent) {
// 404 处理
} else {
renderer.renderToString(vm, function (err, html) {
res.send(html);
});
}
});
const PORT = 8080;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`服务器启动在 ${PORT} 端口`);
});
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
/*
客户端渲染 - 入口
*/
import { createApp } from './index';
const { vm } = createApp();
vm.$mount('#app');
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>这里是模板</h1>
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</div>
<script src="/build.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
|
执行 yarn build-client 编译客户端;
执行 yarn build-server 编译服务端;
执行 node ./server.bundle.js 启动服务器,打开浏览器输入网址 http://localhost:8080/;
|