C++11的函数包装器std::function使用
C++中的函数包装器(Function Wrapper)是用来封装和管理函数或可调用对象(如函数指针、函数对象、Lambda 表达式等)的工具。它们使得函数的使用更为灵活和通用,常被用于异步编程、事件处理
|
C++中的函数包装器(Function Wrapper)是用来封装和管理函数或可调用对象(如函数指针、函数对象、Lambda 表达式等)的工具。它们使得函数的使用更为灵活和通用,常被用于异步编程、事件处理、回调等场景。 C++11引入的 std::function 是最常用的函数包装器。它可以存储任何可调用对象并提供统一的调用接口。以下是关于函数包装器的详细讲解,包括它的基本用法、特点、限制、以及与其他相关机制的对比。 一、std::function 的基本用法std::function 是 C++ 标准库中的一个模板类,可以存储一个可调用对象,如普通函数、函数指针、Lambda 表达式、或实现了 operator() 的对象。 1. 基本语法
二、如何使用 std::function1. 存储不同类型的可调用对象std::function 可以存储任何可以调用的对象,包括函数、Lambda 表达式和函数对象。
2. 使用类型推导C++14引入了泛型Lambda,进一步增强了 std::function 的灵活性:
三、特点与限制1. 类型安全std::function 提供强类型安全,确保传递的可调用对象与指定的函数签名相符。 2. 存储开销std::function 是一个类型擦除(Type Erasure)机制的实现,它会根据保存的可调用对象的类型动态分配内存。尽管这使得类型更灵活,但也增加了一些运行时开销。 3. 性能考虑由于类型擦除的特性,std::function 的性能通常低于直接使用函数指针或 Lambda 表达式,特别是在高频调用的场景下。如果对性能有较高要求,建议直接使用函数指针或模板。 四、结合 std::bindstd::bind 是一个C++11引入的函数适配器,允许将某些参数绑定到函数对象或 Lambda 表达式。与 std::function 结合使用可以使代码更灵活。
五、结合标准库的异步操作在使用异步处理时,std::function 可以存储要在新线程中执行的函数。
|
您可能感兴趣的文章 :
-
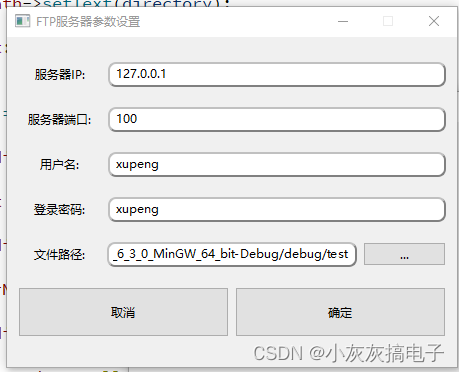
利用Qt实现FTP服务器并支持多客户端登录
一、效果展示 二、源码实现 由于源码较多,只分享其中一部分 ftpserverwidget.h 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3 -
C++11的函数包装器std::function使用
C++中的函数包装器(Function Wrapper)是用来封装和管理函数或可调用对象(如函数指针、函数对象、Lambda 表达式等)的工具。它们使得函数的 -
C++指针和对象成员访问的区别:`.` 与 `->` 的使
在学习 C++ 时,常常会遇到访问对象成员的两种符号:.和-。这两个符号看似简单,但它们的正确使用却需要理解指针和对象的本质差异。对 -
C++中std::thread{}和std::thread()用法
std::thread{}和std::thread()用法 在C++中,std::thread是用于处理线程的类。 关于std::thread{}和std::thread()的区别,主要涉及到C++11引入的统一初始化( -
Qt实现日志文件的滚动写入
Qt 日志文件的滚动写入 flyfish 日志文件的滚动写入功能。在日志文件达到10MB时创建新的日志文件,并且在总日志文件大小达到10GB时开始覆盖 -
Java打印星号图案和数字图案的代码
使用循环和控制语句打印图案 在 Java 中,使用循环和控制语句是打印图案的最佳方法。循环可以帮助你重复执行一段代码,直到满足某个条 -
C++的dynamic代码介绍
在C++编程中,dynamic_cast是处理多态类型转换的关键工具,允许在复杂继承结构中安全地将基类指针或引用转换为派生类指针或引用。通过利
-
基于Matlab实现多目标粘液霉菌算法的
2022-05-14
-
C语言实现可排序通讯录的代码
2021-11-29
-
C++11语法之右值引用的介绍
2022-04-04
-
C语言之水仙花数的介绍
2021-11-25
-
WPF中的导航框架的介绍
2022-06-24