使用这些有用的 Python 代码片段提升你的编程技能,在本文中,我将分享 20 个 Python 代码片段,以帮助你应对日常编程挑战,你可能已经知道其中一些片段,但其他片段对你来说,有可能是新的。我们现在开始吧。
1. 简单的 HTTP Web 服务器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
# Simple HTTP SERVER
import socketserver
import http.server
PORT = 8000
handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
with socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), handler) as http:
print("Server Launch at Localhost: " + str(PORT))
http.serve_forever()
# Type in http://127.0.0.1:8000/ in your webbrowser
|
2.单行循环List
|
1
2
3
4
|
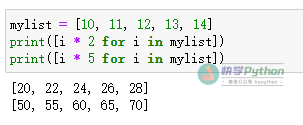
# 单行循环List
mylist = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
print([i * 2 for i in mylist]) # [20, 22, 24, 26, 28]
print([i * 5 for i in mylist]) # [50, 55, 60, 65, 70]
|
Output:
3.更新字典
|
1
2
3
4
|
# Update Dictionary
mydict = {1: "Python", 2: "JavaScript", 3: "Csharp"}
mydict.update({4: "Dart"})
print(mydict) # {1: 'Python', 2: 'JavaScript', 3: 'Csharp', 4: 'Dart'}
|
4.拆分多行字符串
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# Split Multi Lines String
string = "Data \n is encrpted \n by Python"
print(string)
splited = string.split("\n")
print(splited)
|
Output:

5. 跟踪列表中元素的频率
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
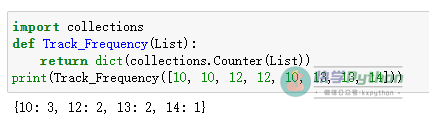
# Track Frequency
import collections
def Track_Frequency(List):
return dict(collections.Counter(List))
print(Track_Frequency([10, 10, 12, 12, 10, 13, 13, 14]))
|
Output:
6. 不使用 Pandas 读取 CSV 文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
# Simple Class Creation
import csv
with open("Test.csv", "r") as file:
read = csv.reader(f)
for r in read:
print(row)
# Output
# ['Sr', 'Name', 'Profession']
# ['1', 'Haider Imtiaz', 'Back End Developer']
# ['2', 'Tadashi Wong', 'Software Engineer']
|
7. 将列表压缩成一个字符串
|
1
2
3
4
|
# Squash list of String
mylist = ["I learn", "Python", "JavaScript", "Dart"]
string = " ".join(mylist)
print(string) # I learn Python JavaScript Dart
|
8. 获取列表中元素的索引
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
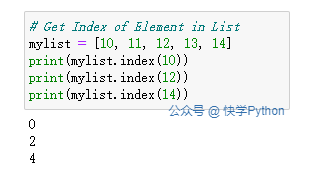
# 获取列表中元素的索引
mylist = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
print(mylist.index(10))
print(mylist.index(12))
print(mylist.index(14))
|
运行结果:
9. Magic of *arg
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
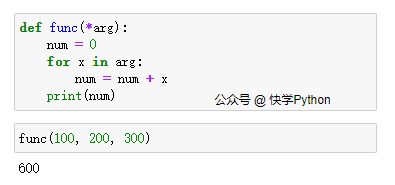
# Magic of *arg
def func(*arg):
num = 0
for x in arg:
num = num + x
print(num) # 600
func(100, 200, 300)
|
运行结果:
10. 获取任何数据的类型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# Get Type of Any Data
data1 = 123
data2 = "Py"
data3 = 123.443
data4 = True
data5 = [1, 2]
print(type(data1)) # <class 'int'>
print(type(data2)) # <class 'str'>
print(type(data3)) # <class 'float'>
print(type(data4)) # <class 'bool'>
print(type(data5)) # <class 'list'>
|
11.修改打印功能
|
1
2
3
4
|
# 修改打印功能
print("Top Programming Languages are %r, %r and %r" % ('Py', 'Js', 'C#'))
# Output
# Top Programming Languages are 'Py', 'Js' and 'C#'
|
12. 字符串去大写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
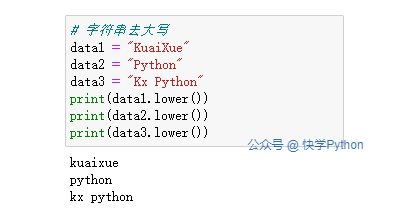
# 字符串去大写
data1 = "KuaiXue"
data2 = "Python"
data3 = "Kx Python"
print(data1.lower())
print(data2.lower())
print(data3.lower())
|
运行结果:
13. 更快捷的变量交换方式
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# Quick Way to Exchange Variables
d1 = 25
d2 = 50
d1, d2 = d2, d1
print(d1, d2) # 50 25
|
14. 分色打印
|
1
2
3
|
# Print with Seperation
print("Py", "Js", "C#", sep="-") # Py-Js-C#
print("100", "200", "300", sep="x") # 100x200x300
|
15. 获取网页 HTML 数据
|
1
2
3
4
|
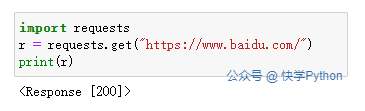
# First Install Request with pip install requests
import requests
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/")
print(r)
|
运行结果:
16. 获取数据占用的内存
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# Get Memory taken by data
import sys
def memory(data):
return sys.getsizeof(data)
print(memory(100)) # 28
print(memory("Pythonnnnnnn")) # 61
|
17. 简单的类创建
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
# Simple Class Creation
class Employee:
def __init__(self, empID):
self.empID = empID
self.name = "Haider"
self.salary = 50000
def getEmpData(self):
return self.name, self.salary
emp = Employee(189345)
print(emp.getEmpData()) # ('Haider', 50000)
|
18. 字符串乘法器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
# String Multiplier
# Normal way
for x in range(5):
print("C#")
# Good way
print("C# "*5) # C# C# C# C# C#
|
19.进行链式比较
|
1
2
3
4
|
# Chain Comparison
a = 5
print(1 == a < 2) # False
print(2 < 3 < 6 > a) # True
|
20. 数字化整数值
|
1
2
3
4
|
# Digitizing
integer = 234553
digitz = [int(i) for i in str(integer)]
print(digitz) # [2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 3]
|
|