Python连接和操作Elasticsearch
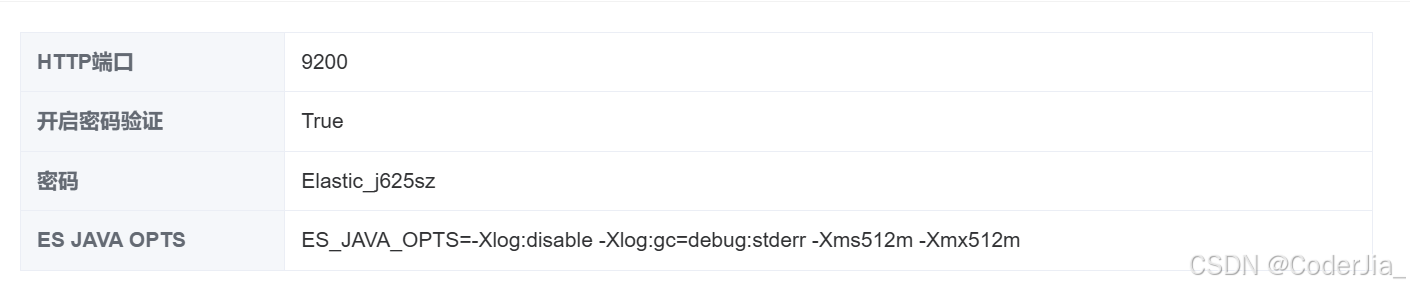
一、服务器端配置 在开始之前,确保你的 Elasticsearch 服务已经在服务器上正确安装和配置。 以下是一些基本的配置步骤: 1. 修改 Elasticsearch 配置文件 找到 Elasticsearch 的配置文件elasticsearch.y
一、服务器端配置在开始之前,确保你的 Elasticsearch 服务已经在服务器上正确安装和配置。
以下是一些基本的配置步骤: 1. 修改 Elasticsearch 配置文件找到 Elasticsearch 的配置文件 elasticsearch.yml,并进行如下修改,以允许远程访问:
2. 开放防火墙端口确保服务器的防火墙已经开放了 Elasticsearch 的默认端口 9200。如果你使用的是云服务器,也需要在安全组中开放该端口。 你可以通过在浏览器中输入 http://<你的服务器IP>:9200 来测试是否能够正常访问 Elasticsearch。如果配置正确,你应该能看到如下 Elasticsearch 的欢迎页面。
二、本地 Python 连接 Elasticsearch在确保服务器端配置无误后,接下来我们在本地使用 Python 连接到 Elasticsearch。首先,你需要安装 elasticsearch Python 客户端库:
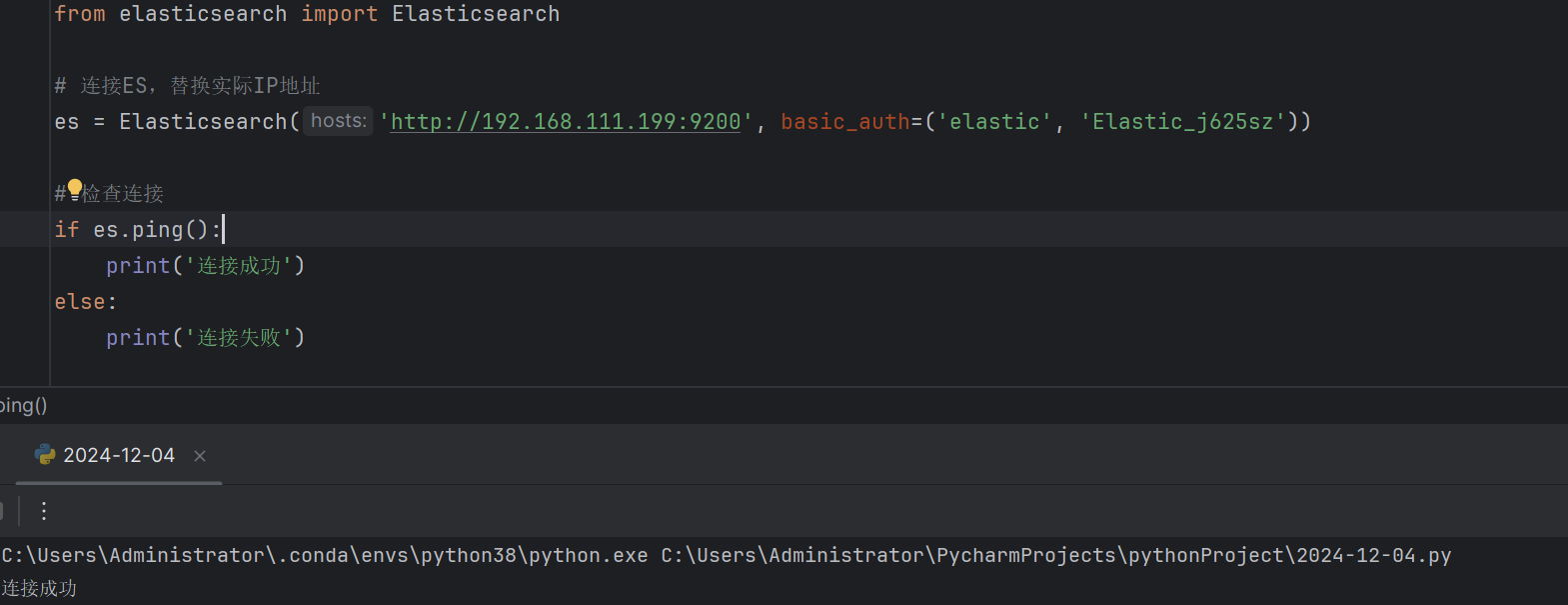
1. 连接 Elasticsearch以下是连接到 Elasticsearch 的示例代码:
在上述代码中,basic_auth 参数用于传递用户名和密码。如果你的 Elasticsearch 没有设置密码,可以省略该参数。
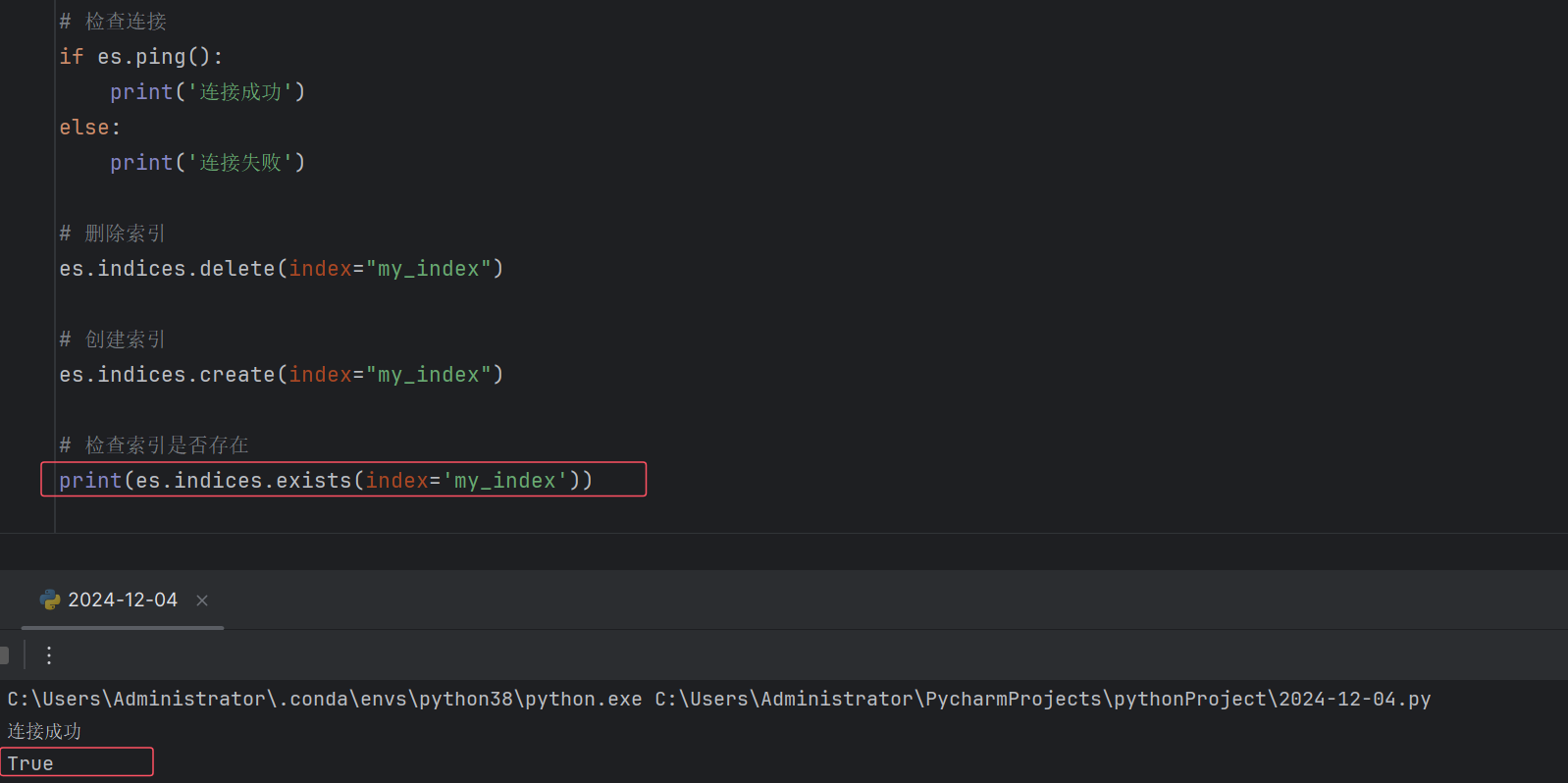
2. 索引操作
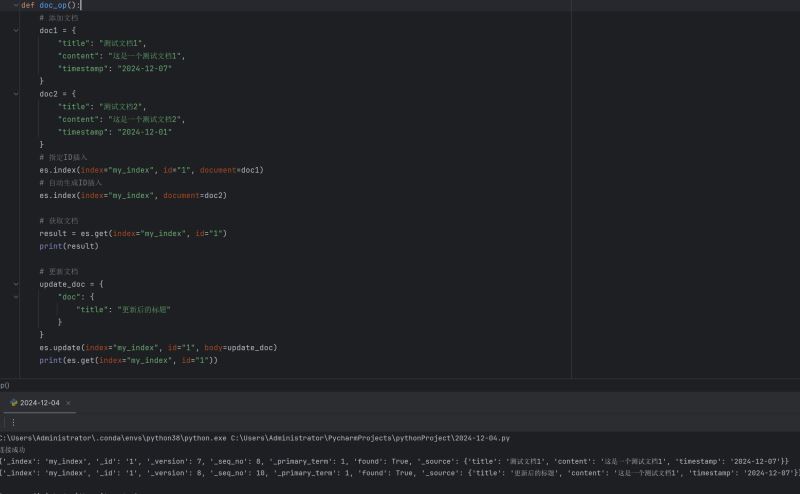
3. 文档操作连接成功后,我们可以开始进行数据存储和搜索操作。以下是一个创建索引并插入数据的示例:
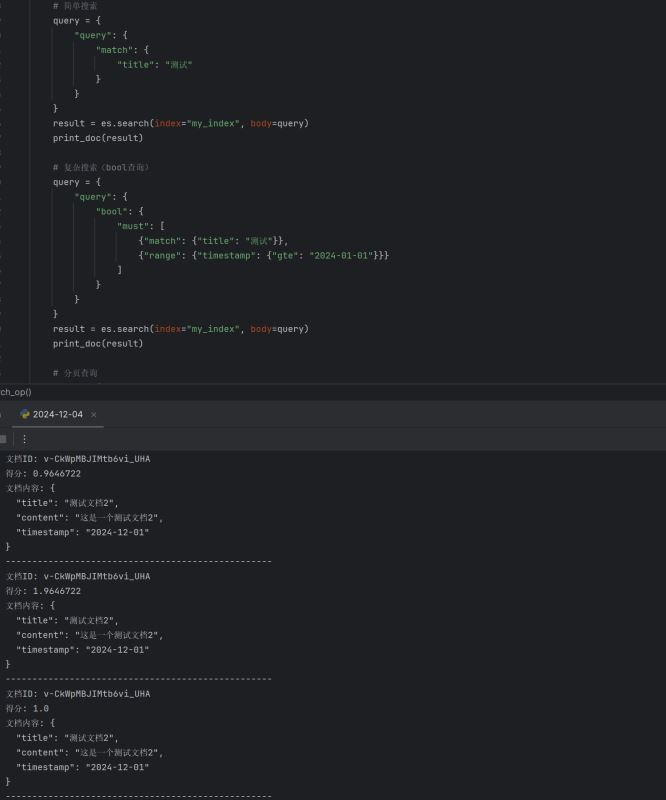
4. 搜索内容接下来,我们可以通过搜索来查找我们存储的数据。 在这之前,定义一个打印文档的方法:
下面是常用的搜索方式:
在这个示例中,我们搜索了包含“测试”这个词的文档,并打印出搜索结果。
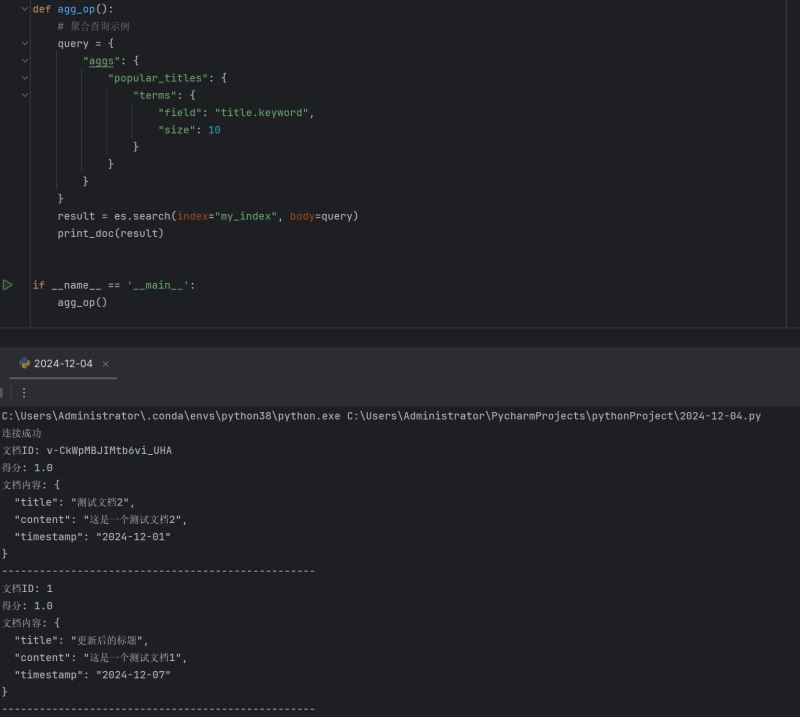
5. 聚合查询
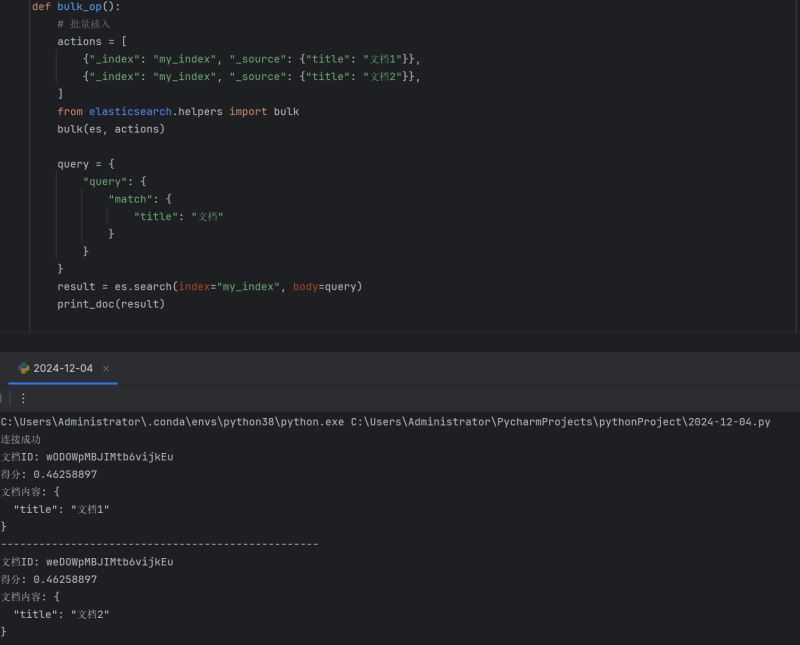
6. 批量操作
三、注意事项在使用 Elasticsearch 时,有几个注意事项需要牢记:
四、故障排除如果在连接或操作 Elasticsearch 时遇到问题,可以尝试以下方法进行排查:
结论通过以上步骤,你应该能够成功使用 Python 连接到 Elasticsearch,并进行基本的文档存储和搜索操作。Elasticsearch 提供了强大的搜索能力,结合 Python 的灵活性,可以帮助你构建高效的数据检索系统。希望这篇文章能帮助你更好地理解如何使用 Python 操作 Elasticsearch。 |
您可能感兴趣的文章 :
-
Python中的下划线“_”们介绍
随便拿一份Python代码,几乎都可以看到很多_的身影。 在Python中,下划线(_)有多种用途和含义,具体取决于它们的位置和使用方式。在这 -
OpenCV-Python给图像去除水印多种方法
去除水印的过程与添加水印相反,它涉及到图像修复、颜色匹配和区域填充等技术。OpenCV-Python 提供了多种方法来处理不同类型的水印,包括 -
Python连接和操作Elasticsearch
一、服务器端配置 在开始之前,确保你的 Elasticsearch 服务已经在服务器上正确安装和配置。 以下是一些基本的配置步骤: 1. 修改 Elasticse -
python随机种子ranrandom seed的使用介绍
在Python中启用随机种子(random seed)是为了确保你的随机数生成过程是可重复的。通过设置随机种子,你可以保证每次运行代码时生成的随机 -
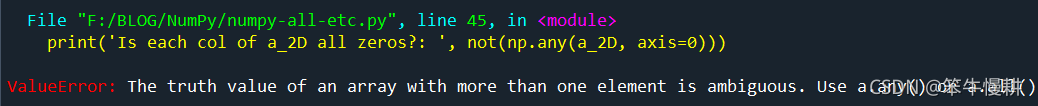
Numpy判断数组是否全0的三种方法
1numpy.any() numpy.any()函数用于检查一个numpy数字是否存在任何一个非0元素,因此将numpy.any()的结果取反即得numpy数组是否全0的结果。例如: 1 -
python实现字符串逆序输出的几种方法
方法一:使用切片(Slicing) 1 2 3 4 5 6 def reverse_string(s): return s[::-1] s=str(input(请输入字符串:)) reversed_string=reverse_string(s) print(reversed_string) 在 -
python删除目录的三种方法介绍
一、os.rmdir(path) 删除目录 path,path必须是个空目录,否则抛出OSError异常。 二、os.removedirs(path) 递归地删除目录。要求每一级目录都为空,才 -
Python内置模块UUID的具体使用介绍
uuid模块是Python标准库的一部分,它提供了一种生成通用唯一识别码(Universally Unique Identifier,简称UUID)的方法,UUID是一种标识符标准,其目的 -
Python中find()的用法小结
1 2 3 s = Hello Word! a = o print ( 字符o在字符串中的索引为: ,s.find(a)) #输出结果为字符o在字符串中的索引为: 4 1 2 3 4 5 s = Hello Word! a = o print (
-
python批量下载抖音视频
2019-06-18
-
利用Pyecharts可视化微信好友的方法
2019-07-04
-
python爬取豆瓣电影TOP250数据
2021-05-23
-
基于tensorflow权重文件的解读
2021-05-27
-
解决Python字典查找报Keyerror的问题
2021-05-27