在开发中,我们会遇到需要延时任务的业务场景,例如:用户下单之后未在规定的时间内支付成功,该订单会自动取消; 用户注册成功15分钟后,发消息通知用户;还有比如到期自动收货,超时自动退款等都是类似的延时任务的业务问题。
这里主要介绍一下几种方法:
- 1、定时任务
- 2、JDK延迟队列 DelayQueue
- 3、redis过期监听
- 4、Redisson分布式延迟队列
- 5、RocketMQ延迟消息
- 6、RabbitMQ死信队列
1、定时任务
写一个定时任务,定期扫描数据库中的订单,如果时间过期,就取消这个订单。这种实现方法成本低、实现容易。这里使用@Scheduled注解实现,也可以用Quartz框架实现定时任务。
|
1 2 3 4 |
@Scheduled(cron = "30 * * * * ?") public void scanOrder(){ orderService.scanOrder(); //每30秒扫描数据库 找出过期未支付的订单,取消该订单 } |
优点:实现容易,成本低,不依赖其他组件。
缺点:
- 时间不够精确。因为扫描是有间隔的,但却随时会产生过期的订单,所以可能会导致有些订单已经过期了一段时间后才被扫描到。
- 增加了数据库的压力。频繁的访问数据库,当数据越来越多时,访问数据库的成本也会增加。
2、JDK延迟队列 DelayQueue
DelayQueue是JDK提供的一个无界队列,它的本质是封装了一个PriorityQueue(优先队列), PriorityQueue内部使用完全二叉堆来实现队列排序,在向队列中插入元素时,需要给出这个元素的Delay时间,也就是过期时间,队列中最小的元素会被放在队首,队列中的元素只有到了Delay时间才允许从队列中取出。
具体的实现思路就是:首先创建一个实体类实现Delay接口,然后将它放入DelayQueue队列中。
(1)定义实现Delayed接口的实体类
需要实现Delayed接口的两个方法:getDelay()和compareTo()
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.util.concurrent.Delayed; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class MyDelay implements Delayed { private String orderNumber; //订单编号 @JsonFormat(locale = "zh", timezone = "GMT+8", pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") private Long time; //过期时间 @Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit timeUnit) { return time - System.currentTimeMillis(); } @Override public int compareTo(Delayed delayed) { MyDelay myDelay = (MyDelay)delayed; return this.time.compareTo(myDelay.getTime()); } } |
(2)将延时任务放入队列
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
package com.demo; import com.demo.config.MyDelay; import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue; public class demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyDelay myDelay1 = new MyDelay("0001", 5L); MyDelay myDelay2 = new MyDelay("0002", 10L); MyDelay myDelay3 = new MyDelay("0003", 15L); DelayQueue<MyDelay> delayDelayQueue = new DelayQueue<MyDelay>(); delayDelayQueue.add(myDelay1); delayDelayQueue.add(myDelay2); delayDelayQueue.add(myDelay3); while (delayDelayQueue.size()!=0) { /** * 取队列头部元素是否过期 */ //DelayQueue的put/add方法是线程安全的,因为put/add方法内部使用了ReentrantLock锁进行线程同步。 // DelayQueue还提供了两种出队的方法 poll() 和 take() , // poll() 为非阻塞获取,没有到期的元素直接返回null; // take() 阻塞方式获取,没有到期的元素线程将会等待。 MyDelay order = delayDelayQueue.poll(); if(order!=null) { System.out.println("订单编号:"+order.getOrderNumber()+",超时取消!"); } Thread.sleep(1000); } } } |
优点:不依赖任何第三方组件,实现方便。
缺点:因为DelayQueue是基于JVM的,如果放入的订单过多,会造成JVM溢出。如果JVM重启了,那所有的数据就丢失了。
3、redis过期监听
redis是一个高性能的key,value数据库,除了用作缓存之外,它还提供了过期监听的功能。
在redis.conf中配置
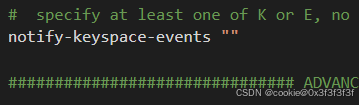
配置notify-keyspace-events "Ex" 即可开启此功能。
springboot 项目集成redis配置过期监听
在pom中引入依赖
|
1 2 3 4 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> |
在yml中配置redis源
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
redis: #数据库索引 database: 0 host: 127.0.0.1 port: 6379 password: 123456 jedis: pool: #最大连接数 max-active: 15 #最大阻塞等待时间(负数表示没限制) max-wait: -1 #最大空闲 max-idle: 15 #最小空闲 min-idle: 0 #连接超时时间 timeout: 10000 |
编写redis配置类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
package com.example.study_demo.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer; /** * Redis配置 */ @Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Autowired private RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory; @Bean public RedisMessageListenerContainer redisMessageListenerContainer() { RedisMessageListenerContainer redisMessageListenerContainer = new RedisMessageListenerContainer(); redisMessageListenerContainer.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return redisMessageListenerContainer; } @Bean public KeyExpiredListener keyExpiredListener() { return new KeyExpiredListener(this.redisMessageListenerContainer()); } } |
编写redis工具类
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 |
package com.example.study_demo.utils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundSetOperations; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; @Component public class RedisCache { @Autowired public RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /** * 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等 * * @param key 缓存的键值 * @param value 缓存的值 */ public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value); } /** * 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等 * * @param key 缓存的键值 * @param value 缓存的值 * @param timeout 时间 * @param timeUnit 时间颗粒度 */ public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit); } /** * 设置有效时间 * * @param key Redis键 * @param timeout 超时时间 * @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败 */ public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout) { return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } /** * 设置有效时间 * * @param key Redis键 * @param timeout 超时时间 * @param unit 时间单位 * @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败 */ public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit) { return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit); } /** * 获得缓存的基本对象。 * * @param key 缓存键值 * @return 缓存键值对应的数据 */ public <T> T getCacheObject(final String key) { ValueOperations<String, T> operation = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); return operation.get(key); } /** * 删除单个对象 * * @param key */ public boolean deleteObject(final String key) { return redisTemplate.delete(key); } /** * 删除集合对象 * * @param collection 多个对象 * @return */ public long deleteObject(final Collection collection) { return redisTemplate.delete(collection); } /** * 缓存List数据 * * @param key 缓存的键值 * @param dataList 待缓存的List数据 * @return 缓存的对象 */ public <T> long setCacheList(final String key, final List<T> dataList) { Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList); return count == null ? 0 : count; } /** * 获得缓存的list对象 * * @param key 缓存的键值 * @return 缓存键值对应的数据 */ public <T> List<T> getCacheList(final String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, -1); } /** * 缓存Set * * @param key 缓存键值 * @param dataSet 缓存的数据 * @return 缓存数据的对象 */ public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet(final String key, final Set<T> dataSet) { BoundSetOperations<String, T> setOperation = redisTemplate.boundSetOps(key); Iterator<T> it = dataSet.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { setOperation.add(it.next()); } return setOperation; } /** * 获得缓存的set * * @param key * @return */ public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet(final String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key); } /** * 缓存Map * * @param key * @param dataMap */ public <T> void setCacheMap(final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap) { if (dataMap != null) { redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, dataMap); } } /** * 获得缓存的Map * * @param key * @return */ public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap(final String key) { return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key); } /** * 往Hash中存入数据 * * @param key Redis键 * @param hKey Hash键 * @param value 值 */ public <T> void setCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey, final T value) { redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hKey, value); } /** * 获取Hash中的数据 * * @param key Redis键 * @param hKey Hash键 * @return Hash中的对象 */ public <T> T getCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey) { HashOperations<String, String, T> opsForHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash(); return opsForHash.get(key, hKey); } /** * 删除Hash中的数据 * * @param key * @param hkey */ public void delCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hkey) { HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash(); hashOperations.delete(key, hkey); } /** * 获取多个Hash中的数据 * * @param key Redis键 * @param hKeys Hash键集合 * @return Hash对象集合 */ public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue(final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys) { return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys); } /** * 获得缓存的基本对象列表 * * @param pattern 字符串前缀 * @return 对象列表 */ public Collection<String> keys(final String pattern) { return redisTemplate.keys(pattern); } } |
编写监控类
在代码中继承KeyspaceEventMessageListener ,实现onMessage就可以监听过期的数据量
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
package com.example.study_demo.config; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.KeyExpirationEventMessageListener; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer; @Slf4j public class KeyExpiredListener extends KeyExpirationEventMessageListener { public KeyExpiredListener(RedisMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) { super(listenerContainer); } @Override public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) { String expiredKey = message.toString(); log.info("订单{}过期了", expiredKey); } } |
测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
package com.demo; import com.demo.config.MyDelay; import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue; public class demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { long expire = 5L; //设置过期时间 String key = "0001"; RedisCache redisCache = new RedisCache(); redisCache.setCacheObject(key,"订单过期了"); redisCache.expire(key,expire); } } |
优点:由于redis的高性能,所以在设置以及消费key时的速度可以保证。
缺点: 由于redis的key过期策略的原因,当一个key过期时,无法立刻保证将其删除,自然我们监听事件也无法第一时间消费到这个key,所以会存在一定的延迟。 此外,在redis5.0之前,订阅发布消息并没有被持久化,自然也没有所谓的确认机制,所以一旦消费信息过程中我们的客户端发生了宕机,这条消息就彻底丢失了。
4、Redisson分布式延迟队列
Redisson是一个基于redis实现的Java驻内存数据网络,它不仅提供了一系列的分布式Java常用对象,还提供了许多分布式服务。Redisson除了提供我们常用的分布式锁外,还提供了一个分布式延迟队列RDelayedQueue ,它是一种基于zset结构实现的延迟队列,其实现类是RedissonDelayedQueue,在springboot中整合使用Redisson分布式延迟队列的步骤如下:
引入pom依赖,yml中配置redis连接
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.redisson</groupId> <artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>3.10.5</version> </dependency> |
创建延时队列生产者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
import org.redisson.api.RDelayedQueue; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * 延迟队列生产者 */ @Service public class RDelayQueueProducer { @Autowired private RedissonClient redissonClient; public void addTask(String taskId, long delayTime){ //创建一个延迟队列 RDelayedQueue<String> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(redissonClient.getQueue("my_delayQueue")); //将任务添加到延迟队列,指定延迟时间 delayedQueue.offer(taskId,delayTime,java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } |
创建延时队列消费者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
import org.redisson.api.RDelayedQueue; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * 延迟队列消费者 */ @Service public class RDelayQueueConsumer { @Autowired private RedissonClient redissonClient; public void consumeTask(){ RDelayedQueue<String> delayedQueue = redissonClient.getDelayedQueue(redissonClient.getQueue("my_delayQueue")); while (true){ String poll = delayedQueue.poll(); if(poll!=null){ //收到消息进行处理 System.out.println("收到消息:"+poll); } } } } |
测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
@PostMapping("/test") public void test(){ rDelayQueueProducer.addTask("0001",5); rDelayQueueProducer.addTask("0002",10); rDelayQueueProducer.addTask("0003",15); } |
优点:使用简单,并且其实现类中大量使用lua脚本保证其原子性,不会有并发重复问题。
缺点:需要依赖redis
5、RocketMQ延迟消息
RocketMQ是阿里巴巴开源的一款分布式消息中间件,基于高可用分布式集群技术,提供低延迟的、可靠的消息发布与订阅服务。下面是在springboot中集成RocketMQ延迟消息的步骤:
安装并启动 RocketMQ 服务
可参考RocketMQ 官方文档进行安装和启动
引入依赖
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.rocketmq</groupId> <artifactId>rocketmq-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version> </dependency> |
配置RocketMQ
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
spring: rocketmq: name-server: 127.0.0.1:9876 # RocketMQ NameServer地址 producer: group: my-group # 生产者组名 |
创建消息生产者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import org.apache.rocketmq.spring.core.RocketMQTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class RocketMQProducerService { @Autowired private RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate; public void sendMessage(String topic, String message,long delay) { // 发送延迟消息,延迟级别为16,对应延迟时间为delay rocketMQTemplate.syncSend(topic, message, delay, 16); } } |
创建消息消费者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import org.apache.rocketmq.spring.annotation.RocketMQMessageListener; import org.apache.rocketmq.spring.core.RocketMQListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service @RocketMQMessageListener(topic = "test-topic", consumerGroup = "my-consumer-group") public class RocketMQConsumerService implements RocketMQListener<String> { @Override public void onMessage(String message) { System.out.println("接收到消息: " + message); //检查订单是否支付 } } |
测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class RocketMQTestController { @Autowired private RocketMQProducerService producerService; @GetMapping("/sendMessage") public String sendMessage() { String topic = "test-topic"; String message = "0001"; //发送订单编号到rocketMQ long delay = 3000; producerService.sendMessage(topic, message, delay); return "消息发送成功"; } } |
优点:系统之间完全解耦,只需要关注生产及消费即可。其吞吐量极高。
缺点:RocketMQ是重量级的组件,引入后,随之而来的消息丢失等问题都增加了系统的复杂度。
6、RabbitMQ死信队列
当RabbitMQ中的一条正常信息,因为过了存活时间(ttl过期)、队列长度超限等原因无法被消费时,就会被当成一条死信消息,投递到死信队列。基于这样的机制,我们可以给消息设置一个ttl ,等消息过期就会进入死信队列,我们再消费死信队列即可,这样,就可以达到和RocketMQ一样的效果。springboot集成rabbitMQ的步骤如下:
安装并启动 RabbitMQ 服务
可参考RabbitMQ官方文档进行安装和启动
引入依赖
|
1 2 3 4 |
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> |
配置RabbitMQ
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
spring: rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest |
配置 RabbitMQ 队列和交换机
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; @Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig { public static final String ORDER_EXCHANGE = "order.exchange"; public static final String ORDER_QUEUE = "order.queue"; public static final String ORDER_ROUTING_KEY = "order.routing.key"; public static final String DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "dead.letter.exchange"; public static final String DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE = "dead.letter.queue"; public static final String DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY = "dead.letter.routing.key"; // 死信交换机 @Bean public DirectExchange deadLetterExchange() { return new DirectExchange(DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE); } // 死信队列 @Bean public Queue deadLetterQueue() { return new Queue(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE); } // 绑定死信队列和死信交换机 @Bean public Binding deadLetterBinding() { return BindingBuilder.bind(deadLetterQueue()).to(deadLetterExchange()).with(DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY); } // 正常交换机 @Bean public DirectExchange orderExchange() { return new DirectExchange(ORDER_EXCHANGE); } // 正常队列,设置死信交换机和路由键,以及消息TTL为30分钟(1800000毫秒) @Bean public Queue orderQueue() { Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(); args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE); args.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY); args.put("x-message-ttl", 1800000); return new Queue(ORDER_QUEUE, true, false, false, args); } // 绑定正常队列和正常交换机 @Bean public Binding orderBinding() { return BindingBuilder.bind(orderQueue()).to(orderExchange()).with(ORDER_ROUTING_KEY); } } |
创建消息生产者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMessageProducer { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void sendOrderMessage(String message) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.ORDER_EXCHANGE, RabbitMQConfig.ORDER_ROUTING_KEY, message); } } |
创建消息消费者
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class OrderMessageConsumer { @RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE) public void receiveOrderMessage(String message) { System.out.println("收到订单: " + message); // 模拟检查订单支付状态 } } |
测试
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class OrderMessageController { @Autowired private OrderMessageProducer orderMessageProducer; @GetMapping("/sendOrderMessage") public String sendOrderMessage() { String message = "0001"; //订单编号 orderMessageProducer.sendOrderMessage(message); return "订单消息已发送,30分钟后处理"; } } |
优点:同RocketMQ一样可以使业务解耦。
缺点:RabbitMQ 的 TTL 是基于队列的,而不是基于单个消息的精确时间控制。当队列中有多个消息时,即使某个消息的 TTL 已经过期,也需要等待前面的消息被处理完才能进入死信队列,导致消息的实际处理时间可能会有一定的延迟,无法保证精确的延迟时间。